The political distribution of left and right among young people can also be analyzed from a gender perspective.
- In the last two decades, an ideological distance between genders has spread in the youngest generations of developed countries. More and more young men are approving conservative or far-right ideas and more and more young women and non-binary people are considered progressive and placed on the left. This ideological remoteness, beyond politics, has to do with culture and personal identity. What are the consequences for our societies?

In most countries in the Global West, young people are generally considered to be more progressive and older, more conservative. In recent years, a new axis of articulation of political opinions has been added to age: gender is also taken into account. Today, young women in the West are significantly more progressive than men of the same age. Several studies show that in terms of political opinions, the group of non-binary people has characteristics femeninas.Algunas social trends, spread in EE.UU., spread later in Europe, but in this case it seems that the evolution is parallel – with few regional particularities. In March of this year, the journal The Economist has analyzed data from political surveys of
20 countries, coming from binarism and without specifying data on non-binary, coming from North America, Europe and South Korea, including Asia and the West. According to this analysis, in 2000 there were no gender differences in political opinions. By contrast, in 2020 the gap is clear: 51% of men aged 18 to 29 are considered progressive but 63.5% of women of the same age. In these twenty countries, young women are more progressive than young men.
In the case of Europe, the largest gap is observed in Poland, and is markedly higher than Europe in the US. In addition, it has increased especially in the last decade: In 2008 there were no gender differences, while in the 2022 House of Representatives elections 46% of young men and 28% of young women voted in favour of the republicanos.En Flanders (northern Belgium), the parties most voted by young
men in the last elections were the far-right Vlaams Belang and the right-wing N-VA. Young women will include the green party Groen and Vooruit on the left. In the last elections in Poland, the party most voted by men between the ages of 18 and 29 has been the far-right Confederacy. One of the slogans of this party, which brings together 26% of the votes of young men, is "against feminists, in defense of real women." With this content, it is no wonder that only 6% of the votes of women of the same age have been achieved and that the majority of young women have voted in favour of relegating abortion to the centre-left parties.
Young men, more anti-feminists than older men
According to a survey conducted by the IPSOS in Poland five years ago, women between 18 and 39 years of age see climate change as the greatest risk for Poland. Men of the same age group, on the contrary, consider the LGBT movement and "gender ideology" to be the main risks. In addition to the Polish Confederacy, far-right parties have appeared in several countries with very masculinistic speeches such as Reconquete in France, SALF in Spain or Chega in Portugal, between otros.Segun the daily La croix, an internal motion approved by the Chega party in 2020 recommended to women who had aborted the cutting of the ovaries to do it. Although the motion was withdrawn by several protests, it contributed to opening the window of acceptability.
The study by The Economist magazine shows a remarkable evolution for the 27 European countries: in general, men aged 18-29 years are more anti-feminist than men aged 65 years. They say that the development of women’s rights has gone too far and that makes opportunities for men difficult. The opinion of young women from different countries shows a contrarian evolution. For example, young women in the UK believe that the living conditions of women are worse. In South Korea, the change is most notable: 80% of men between 20 and 30 years old say they are discriminated against as men, but only 30% of men over 60 years old.
Different perceptions of social changes
In the West, after a long absence of higher education, women are now more qualified than men, especially in young generations. Although this does not, for the time being, have proportional effects on employment and wages, women today have a more informed view of social dynamics. In addition, sociologists tend to relate the passage through university with a more progressive and egalitarian perspective. In rich countries, common sexism has regressed in recent decades, and women and men may have a different perception in their daily lives: more freedom for some, more adaptation to the new rules for others, with or without enthusiasm. Social networks multiply the contrasting perception of these long-term evolutions, in which each user reinforces their opinions in their "social bubble", which can be one of the culprits of the growing polarization.
According to a study conducted in the United States by the Survey Center on American Life, generations born in the late 1990s and early 2000s have more difficulty establishing relationships and say they feel lonely that they feel more than the previous generation. 31% of women and only 16% of men declare themselves LGBT. These proportions are higher than those of previous generations, with the gender gap even greater. The fact that there are as many women as today do not want to live with men, and that they can live without marriage, is historically new.
Against this trend, of course, extreme right-wing masculinist parties and the human sphere dare to end feminism and the LGBT movement, in the name of "traditional values," and create more white-skinned children. Anti-feminism is one of the links of the extreme right. The solution to this development is not simple. How do we make younger people understand that male norms also harm young men and boys and that the LGBT movement does not pose a risk to them? How do you understand that climate change and care are real challenges?
These two opposing movements in younger generations, beyond politics, have to do with culture and personal identity, so they're so profound. Therefore, solving this gap will necessarily require profound changes.
Pasa den asteko "kaleratze ilegala" salatu dute hainbat herritarrek, ostiral arratsaldean.
Manifestazio jendetsu batek herriko kaleak zeharkatu ditu, Poliziaren gehiegizko dispositibo batek zainduta, gazteek kudeatutako guneen defentsan eta Gaztetxeak erasoen aurrean defendatzeko. Manifestazioaren amaieran, publiko egin dute iragarpena.
Hezkuntza Sailak EITBri azaldu dioenez, ikastetxe bakoitzean izan beharreko baliabideak batzar teknikoetan negoziatu partez, mahai negoziatzailean landu beharko lituzkete. Bihar eta etzi greba egingo dute EAEko ikastetxe publikoetako irakasleek.
Etxebizitza eskuratzeko orduan pertsona arrazializatuek eta migratzaileek jasaten duten bazterketa sistematikoa salatu dute Gasteizen, agerraldi baten bidez. Apirilaren 5ean Donostiara bertaratzera deitu dute, etxebizitza-eskubide unibertsalaren alde.
Usurbil herri zaintzaileagoa izateko lankidetzan ari diren herrikide, eragile eta erakundeen talde argazkia duzue albiste honi atxikitakoa. Larunbatean Sutegin egindako "Usurbil, herri zaintzailea" izeneko ekitaldian atera genuen. Norabide horretan herri hau egiten ari... [+]
Historia errepikatzen dela idatzi zuen Marxek, “lehenik tragedia gisa, gero fartsa moduan”. Armagintzaren eta militarismoaren inguruan errepikapen hutsa ez, espiralean goraka doan buklea ari gara bizitzen, fartsatik asko duena, eta tragedian amaitzeko gero eta aukera... [+]
Udaberrian orain dela egun gutxi sartu gara eta intxaurrondoa dut maisu. Lasai sentitzen dut, konfiantzaz, bere prozesuan, ziklo berria hasten. Plan eta ohitura berriak hartu ditut apirilean, sasoitu naiz, bizitzan proiektu berriei heltzeko konfiantzaz, indarrez, sormen eta... [+]
Aljeriatik datoz Mohamed eta Said [izenak asmatuak dira], herri beretik. “Txiki-txikitatik ezagutzen dugu elkar, eskolatik”. Ibilbide ezberdinak egin arren, egun, elkarrekin bizi dira Donostian, kale egoeran. Manteoko etxoletan bizi ziren, joan den astean Poliziak... [+]
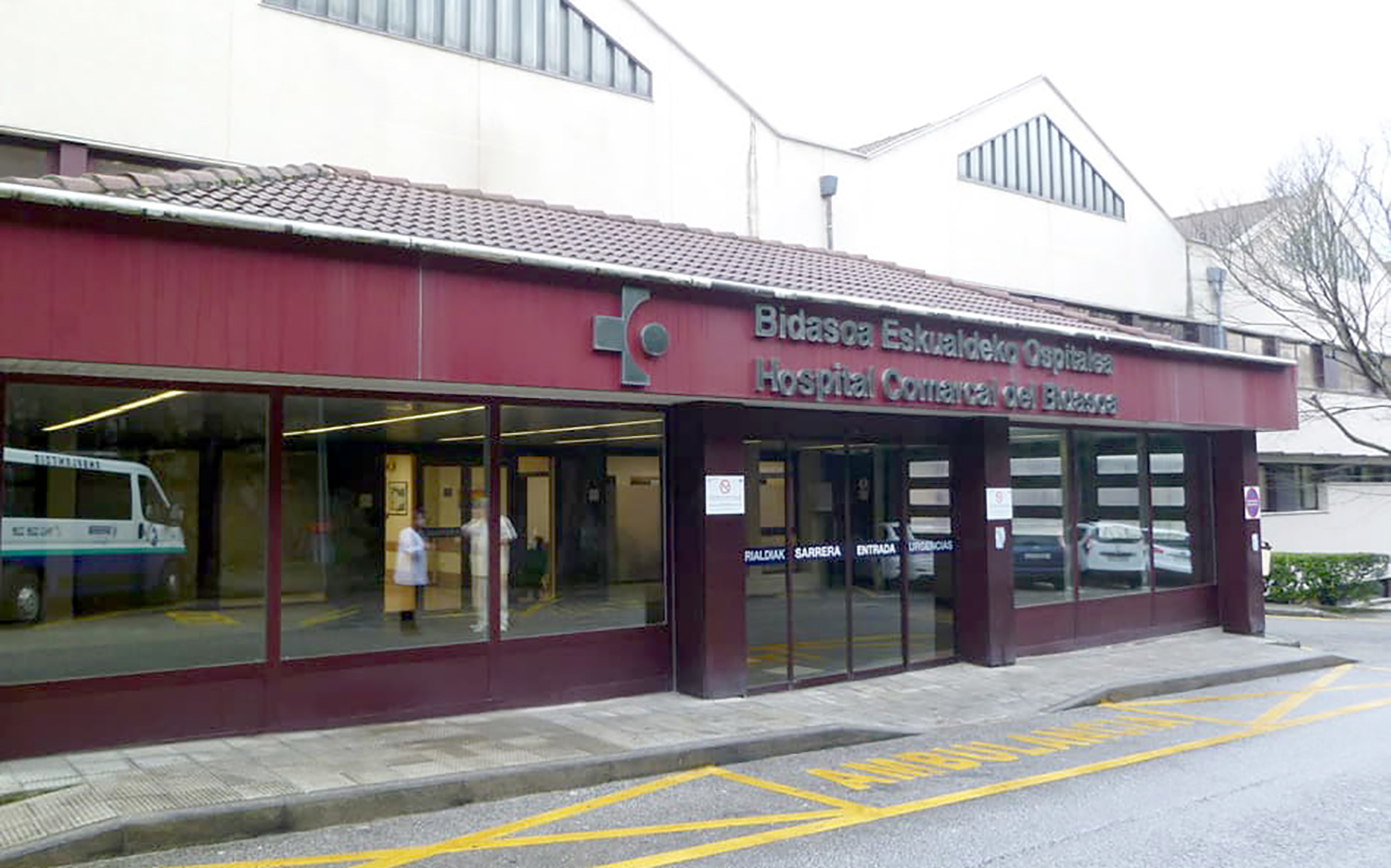
Pazienteek Donostiara joan behar dute arreta jasotzeko. Osasun Bidasoa plataforma herritarrak salatu du itxierak “are gehiago hondatuko” duela eskualdeko osasun publikoa.
Seaska Sarean inklusio egoeran dauden 165 ikasleei laguntza bermatzeko hasi dute kanpaina, antolaketa propioa eratuta. Frantziako Hezkuntza Ministerioaren jarrera salatu dute kanpaina aurkezteko prentsaurrekoan, behar bereziak dituzten haurren inklusiorako baliabide... [+]
Ikerketa parte-hartzailea eta gogoetatsua bultzatzen du Biharamunen Lantegia kooperatibak, eta zientzia eta ikerketa herriarengana hurbiltzeko lan egiten du. Duela urte eta erditik egoitza Bidarten dauka, eta Institut Curie-rekin elkarlanean Iker Herria ikerketa zentroa sortzeko... [+]
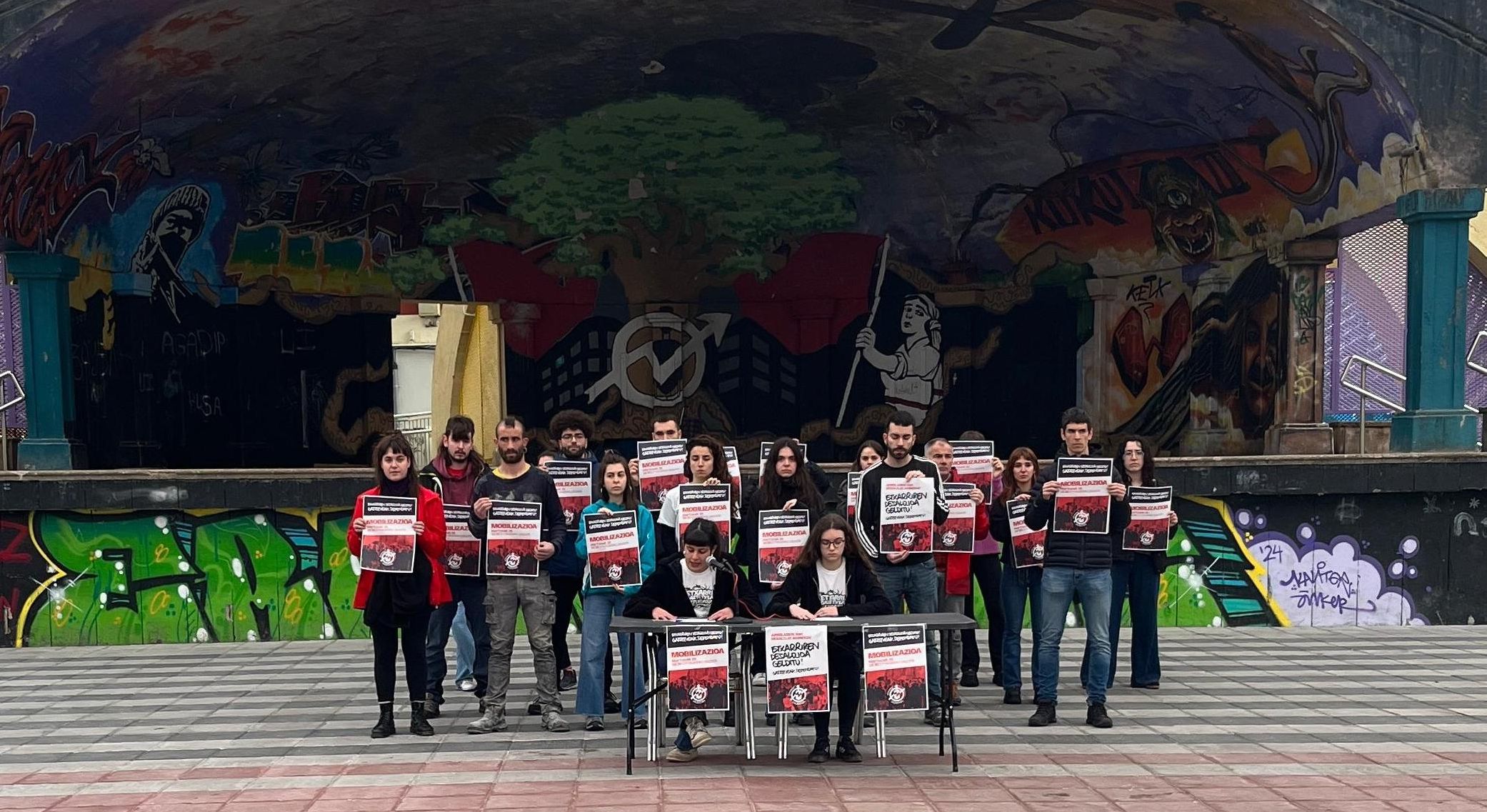
Amenabar enpresak Bilboko Udalaren eskutik apirilaren 4rako agindu duten desalojoaren kontra azaldu dira bilkuran. Poliziak indarrez kanporatu ditu. Ostiral honetan18.30ean, Errekaldeko Plazatik hasiko den manifestaziora batzeko deia luzatu dute gazteek, baita desalojoaren... [+]
Europako Batzordeak aurkeztu duen plana ustezko gerra edo hondamendi baten aurrean “bizirauteko” kit batetik harago doa: hogeita hamar neurri proposatu ditu eskoletan, enpresetan eta herritarren artean militarismoa eta beldurra sustatuko dutenak.
Bilboko Udalak eta Amenabar enpresak proiektu urbanistiko baten pean itxi nahi dute 10 urtez auzoko bizitza sozialaren erdigunea izan den topalekua. Horren aurrean, hiriko 55 kolektibok baino gehiagok manifestu bat sinatu dute prozesua gelditzeko exijitzeko.











.jpg)






