Cultivation has the power to rebalance the unbalanced nitrogen cycle
- In September last year, Science Advances published Earth beyond six of nine planetary boundaries (Earth has exceeded six of the nine planetary boundaries), an update of overcoming the planet's boundaries. The greenhouse effect, the use of fresh water, the use of earth’s crust, biodiversity, chemical pollution and biogeochemical cycles (phosphorus and nitrogen) have already been overcome. The latter, already overcome in the first version of this research in 2009, has a lot to do with cultivation.

Like the carbon cycle, the nitrogen cycle is closely linked to plant biomass. In terrestrial ecosystems, leaves and other plant debris released from plant biomass to the soil feed the soil organic nitrogen reserve. Soil beings (fungi, bacteria, worms, etc.) mineralize this organic nitrogen and the roots of growing plants happen that mineral nitrogen. In addition to this main part of the cycle are the plant consumption of the animals and their subsequent grounding after digestion or after death, the losses of mineral nitrogen produced in the soil and the capture of nitrogen from the atmosphere through legumes that compensate them.
On the contrary, compared to the carbon cycle, the nitrogen cycle is much more connected to the atmosphere: in most situations only 5% comes from the atmosphere with legumes, being most of the cycle in plants and soils. Consequently, if local losses increase and they are unable to compensate for legumes, soil fertility will be reduced. These losses can easily occur because ammonia, nitrate and nitrogen oxidation are very mobile, the first two in air and the last two in water.
Industrial cultivation profoundly transforms the cycle
Nitrogen cycle is open in cultivation systems: in each crop a portion of nitrogen is removed from the system and a compensatory fertilizer is added to the soil. Fertilization in Western Europe was carried out mainly through livestock dejection. In areas with special land capacity, such as the countryside, before planting the great pine grove today, the first function of the animals was the production of excrements, with meat or wool by-products.
The use of legumes in rotations began in the 17th century, improving soil fertility and reducing surface needs. Since the 1820s, aquatic birds of Peruvian repopulations began to export to Europe, increasing their crop yields. But the biggest change occurred in the 20th century, when the German chemist Fritz Haber got air nitrogen to become fertilizer.
Five years later, Carl Bosch, of the company BASF, implemented the discovery of Haber at the industrial level. However, unlike legumes, Haber and Bosch needed large amounts of fossil fuels for this chemical reaction, i.e. to produce ammonia from air nitrogen and hydrocarbon hydrogen. Ammonia was used to produce fertilisers and explosives. During the First World War, Germany quickly developed this sector: In 1913 the first chemical unit produced 11,000 tons, in 1917 a second one was built, 36,000 tons were produced and in the following year 160,000 tons were produced. After the war, these same workshops, and similar workshops built around the world, began to mass-produce synthetic fertilizers. From then on, the uses of polycultures and legumes become obsolete, starting the industrialization and specialization of the crop. Alfred James Lotka, a theorist of population dynamics, said in 1924 that a new era opened in the history of mankind. Although the word "antropozene" was not used at that time, he perceived the importance of change.
Drowned by the nitrogen of the anthropocene
A century after Lotka's comment, synthetic fertilizers penetrate the biosphere more than the amount of nitrogen that the biological nitrogen cycle captures from air. This gigantic change is not taking place without collateral damage to the losses of mineral nitrogen that occur in the soil. These losses are massive if synthetic fertilizers are used.
One reason is that the losses are not proportional to the use of fertilizers, but are proportionally higher if larger amounts of fertilizers are used. On the other hand, nitrogen efficiency is decreasing with the increase in the amount of fertilizers. In addition, nitrate not absorbed by vegetation is poured into groundwater, rivers and coasts, degrading the potability of water and ecosystems. The remaining ammonia is also emitted into the atmosphere, harming our health.
According to the group that has defined planetary boundaries, this nitrogen surplus should be no more than 60 million tonnes a year and today is 190 million tonnes. The UN and the European Union have therefore announced the objective of reducing nitrogen losses by 2030. The problem is that, without leaving the industrial crop, the best way to improve the efficiency of fertilizers and reduce nitrogen losses is to reduce production, as other adjustments, such as avoiding nitrification in soils, improving varieties, making more precise fertilizers, have only marginal effects.
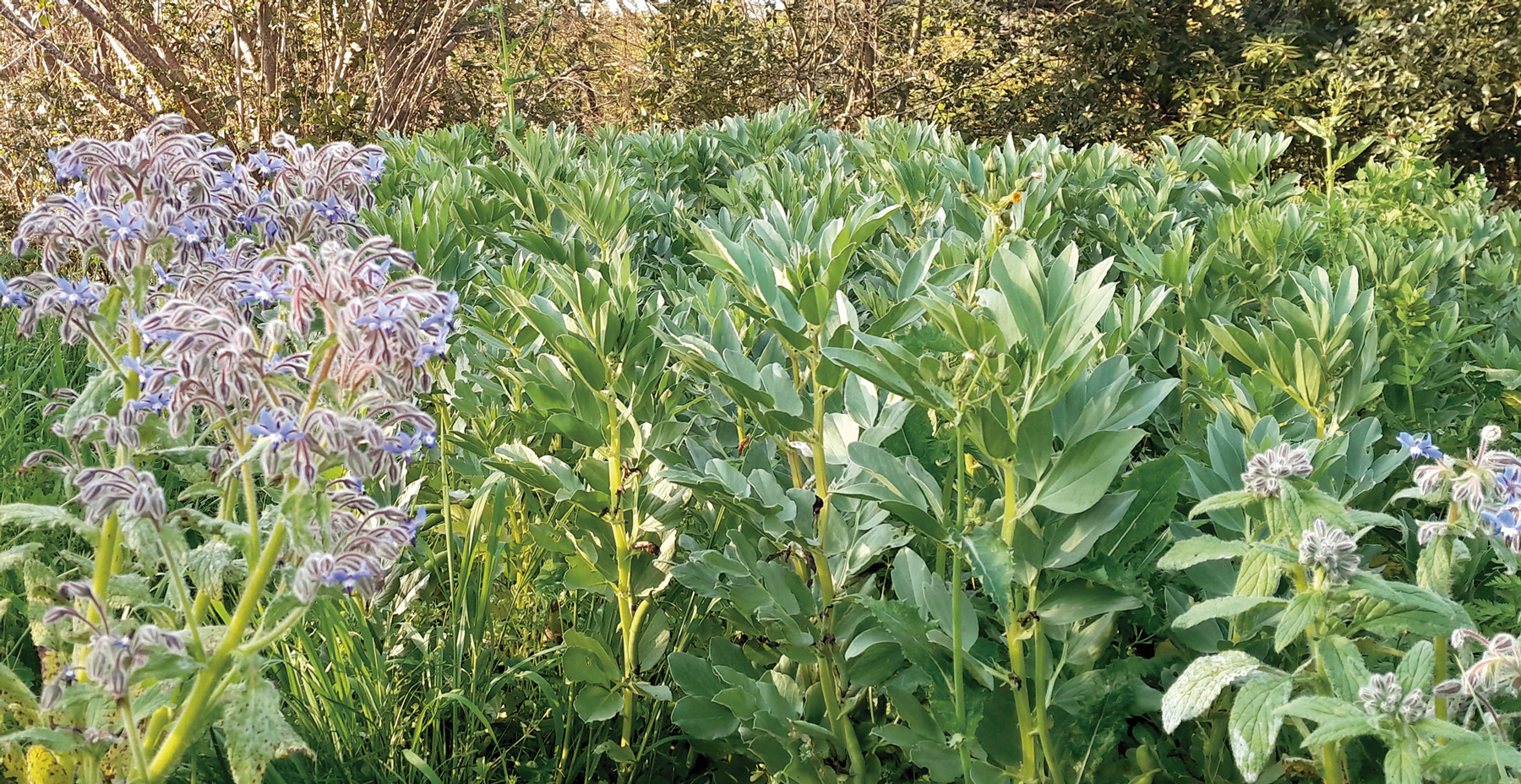
But who is now prepared to reduce production with the tensions on the global cereals market in the last two years? How can we feed those who will soon be 10 billion without compromising the living conditions of future generations? In short, according to three fry: more legumes in rotations (thus increasing the organic nitrogen reserve of the soil); reconnecting crops and cultivation (feeding animals only with local fodder and taking advantage of their excrements in the fields); significantly reducing meat consumption and replacing bridges with crops for human consumption (in order to make the use of soils more efficient). These conclusions are provided by the new study Methodology for designing a European agro-ecological future. To take a paradigmatic illustration: fodder maize produced with synthetic fertilizers instead of exporting it for forage of livestock for industrial breeding; planting wheat, chickpeas, beans, potatoes and trees; matorrals grazing on uncultivable nearby lands, taking advantage of their excrement and reorientation of meat only towards the whims of the weekend.
Unfortunately, there are not many possibilities for reducing nitrogen surpluses, but fortunately the advantages of implementing them are many.
Today’s Venice is built on an archipelago of 118 islands. These islands are connected by 455 bridges. The city is based on mud rather than Lura. Millions of trees in the area were cut down from the 9th century onwards to build piles and cement the city. Years have passed and... [+]
Lehengai anitzekin papera egitea dute urteroko erronka Tolosako Lanbide Heziketako Paper Eskolako ikasleek: platano azalekin, orburuekin, lastoarekin, iratzearekin nahiz bakero zaharrekin egin dituzte probak azken urteotan. Aurtengoan, pilota eskoletan kiloka pilatzen den... [+]