Summer 2021 floods cannot be understood by denouncing climate change and forgetting concrete
- Since mid-June, extraordinary floods have caused pernicious damage in several European regions. Heavy rains and floods have been repeated throughout the summer on all four extremes of the world, such as in China in the African Sahel, Pakistan or the United States, demonstrating that climate change caused by global warming has already begun to occur. There's torrential rain -- on soils that have lost the ability to absorb water.

The Madrid newspaper El País had the following title on 31 August: “The heavy rains suffocate Sahel. Climate change has led to the tripling of violent storms in the south of the Sahara.” In Senegal, hundreds of people drowned in Niger and many sunken buildings, 6,000 houses destroyed in Sudan and land slopes to be channelled into the Nile, the neighbourhoods of the capital of Dakar were completely flooded. According to experts, the rains that have always spread in Sahel during the three summer months are now concentrated in rarer and more violent attacks, hitting strongly: It rains less than in 1950 and 1960, but
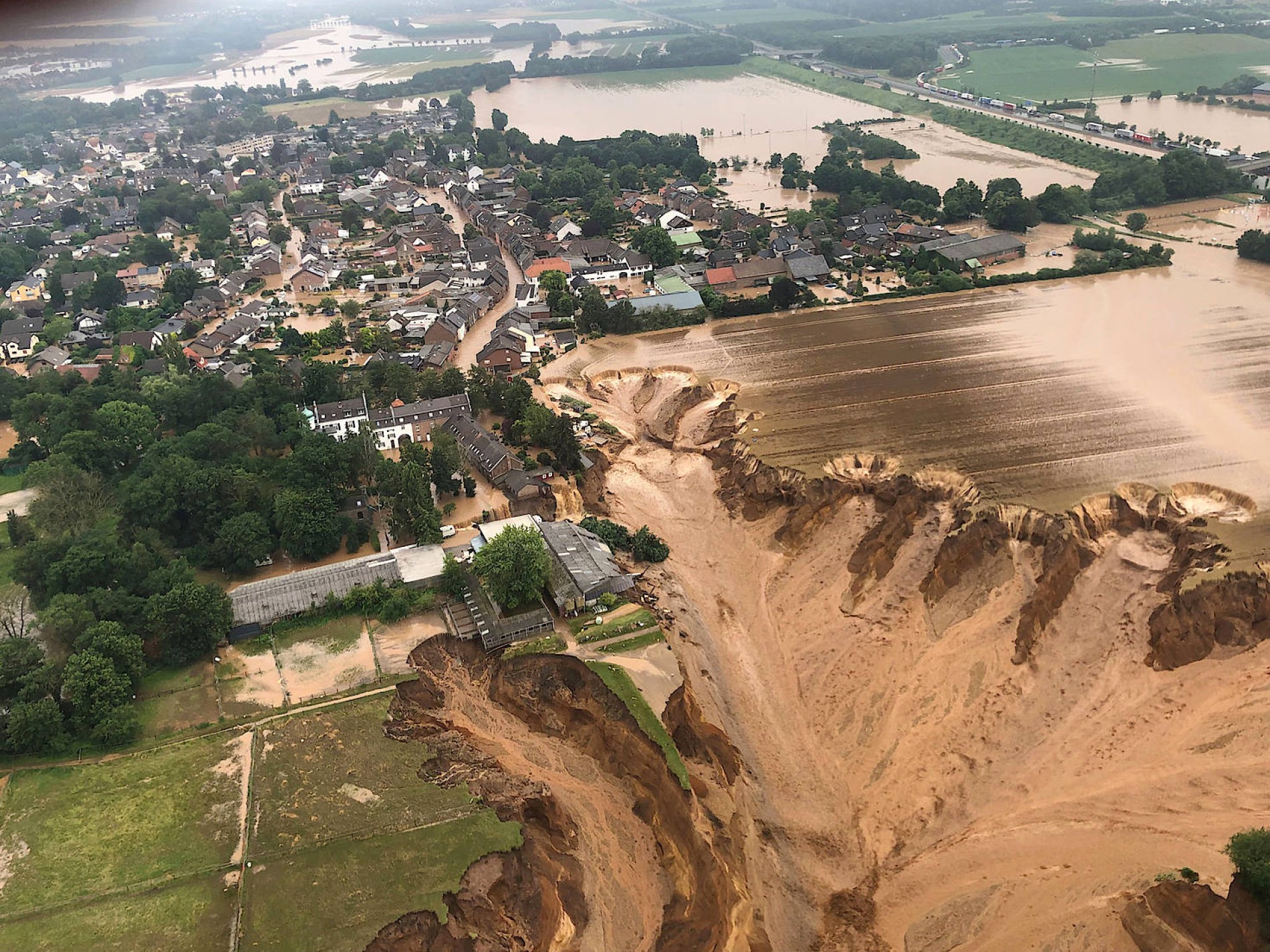
more concentrado.Las news of heavy rains have come around the world throughout the summer of 2021. European floods entered the continent in the days following England on 12 July, with at least 230 deaths in Germany and Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Austria, Italy, Slovenia and Romania.
In addition to the deceased, water has left enormous economic damage in the region, the largest in Germany and Belgium: damage to housing, industry, trade, infrastructure of all kinds and agriculture has been estimated at EUR 2,550 million, counting only those protected by insurance. Who should be charged with this damage?

Firstly,
in Germany, a model of foresight, preparation and order, the basis of the authorities is questioned when they are on the threshold of decisive elections: How has the alert system not worked better?Hannah Clok,
an advisor to the European Flood Monitoring System, made it clear that the organisation alerted all European governments in time to the protocols developed after the 2002 floods: “The alerts, the heavy rains and floods were reported to be taken care of. But the management of this information is the responsibility of the national authorities.” Regarding the determination of the measures to be taken in Germany for
each autonomous region, in the chain of decisions there were ruptures: in one village the authorities did not evacuate in time, in another they ordered the evacuation and some neighbors stayed at home… However, the most effective alert system could not prevent this type of chubascos from terrorizing in a compassionate way.
“In the upper part of the atmosphere, low temperatures have blocked the large bodies of air loaded with water and then they have been poured over the region for four days,” the AFP summed up the July flood by the climatologist Jean Jouzel, vice-president of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
Other complementary phenomena have been commented by the experts: Inertisation of jet stream wind. The trawl current, as Wikipedia explains in Euskera, is a strong, tubular wind that moves west-east around the North Pole at a height of between 9 and 11 km. In our case, the melting of Arctic ice has weakened the Jet Stream, which will also aggravate extreme climate accidents.

BUILDING MORATORIUM Europe
has periodically suffered significant flooding, but this year's one has been special, both because of the number of falls in rainfall and the intensity of the chubascos. Europe is thus aware of one of the consequences of climate change. Along with droughts, fires or rising sea levels, extreme rains and floods are going to become more and more frequent, as experts have reminded us and we have begun to accept little poco.La mechanics of the phenomenon has
been summarized by the scientific journal The Lancet in its summer editorial: “For each degree in which temperature warms up, air can accumulate 7% more moisture and maintain it for longer, causing larger droughts on one side and more intense rains later, releasing moisture, an extreme time model that is considered to worsen with warming.” However, The Lancet’s
editorial continues to say: “In addition to climate change, there are landscape factors that favor flooding, such as the water absorption capacity of the soil, topography and urbanization, which increase the water discharge rate [runoff]”. These are the risks of a misguided urban planning, of a greater use of concrete in a region already populated in Europe: intense rains on soils capable of absorbing less and less agua.El the people of Erftstadt, which we have seen in all the media, have
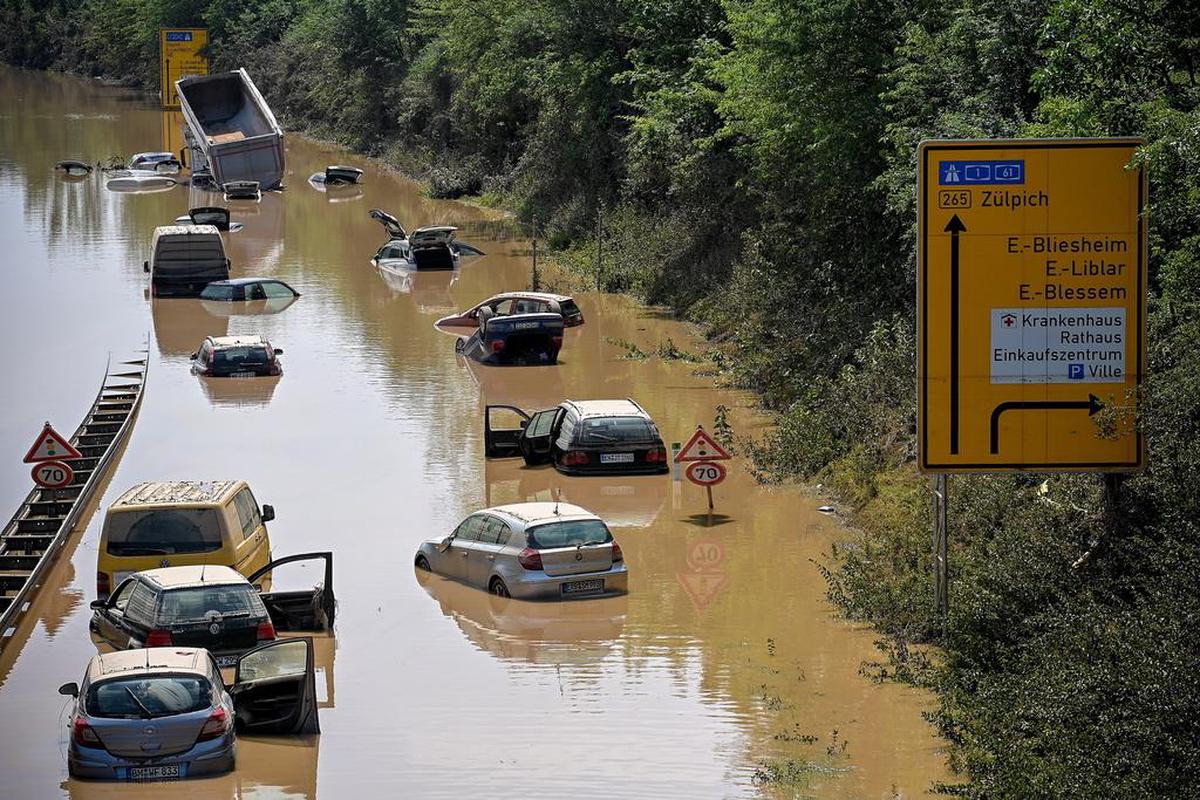
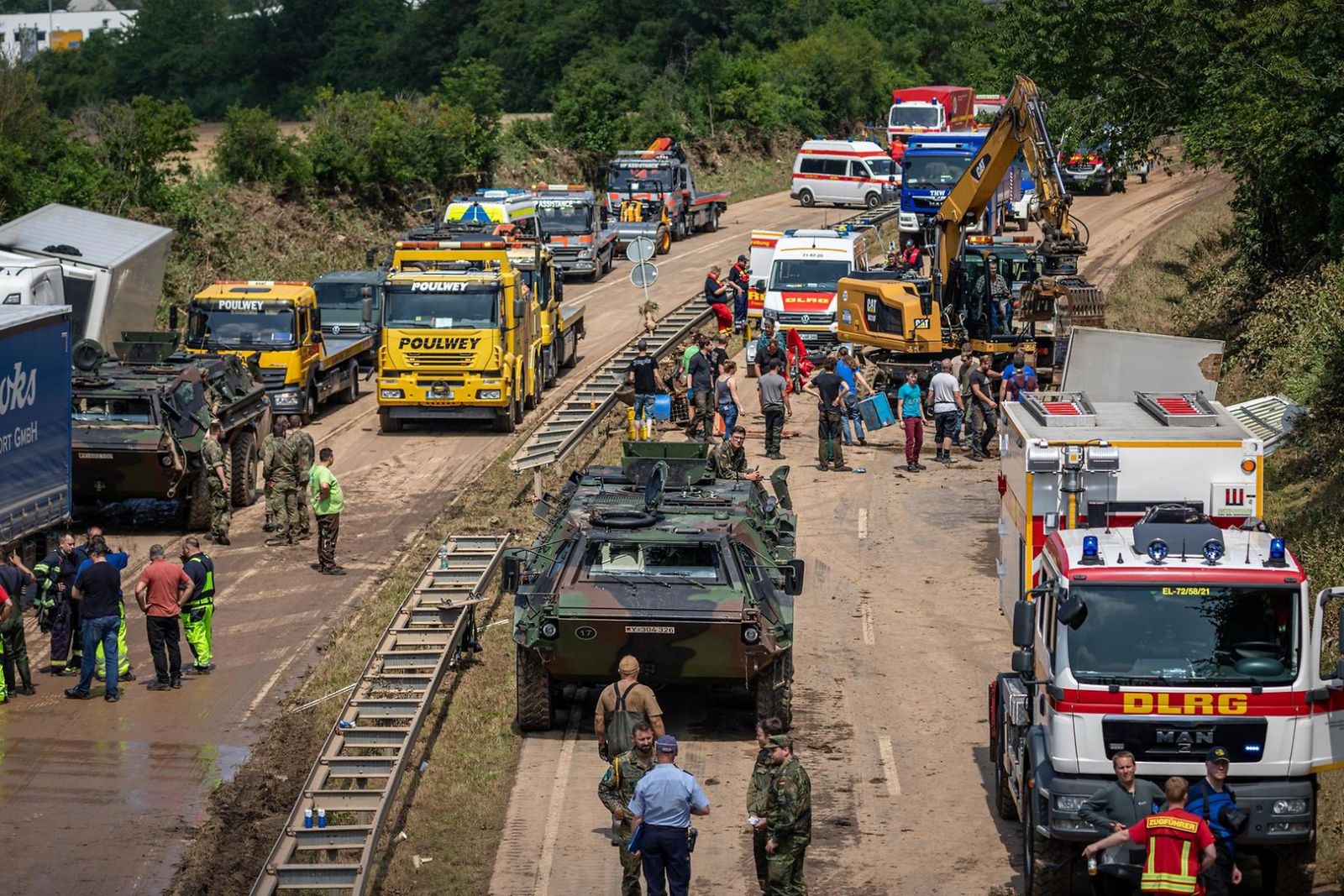
been destroyed by the force of the river and the gigantic lucernaries. When you look at the images, you can't understand how these earthquakes were able to emerge in such a soft spot. In addition to overflowing the regatta, the water drowned the highway passing by the village, where dozens of cars and trucks that the military had to rescue in good days, the waters trapped in the barriers and obstacles of the betons ended up exploding creating new channels.
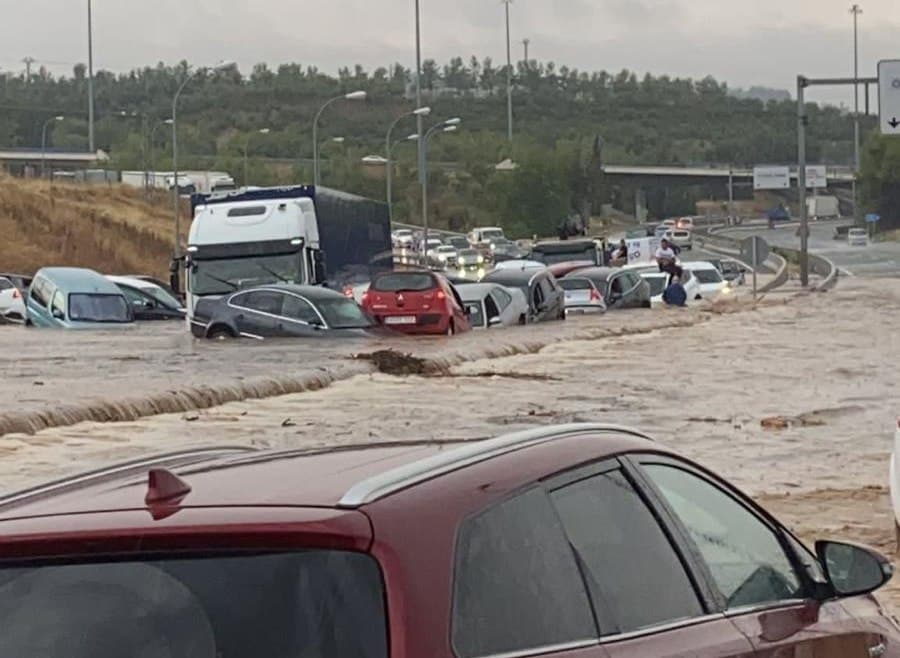

In July,
the greatest problems occurred not only in the large rivers but in the vicinity of the smaller streams that are directed to them. As we have seen in Erftstadt, in European countries the streams have become artificial channels, the concrete has lost the water absorption capacity of the soils and the drainage and water steps necessary for the special torrential rains in the whole area rural.El Dutch architect
Hans Ibelings asked at the end of July for the moratorium of construction in the European Union since the newspaper Barcelona The key information is: “Construction is responsible for 40% of global warming.” The culprit for heavy rains is the one that prevents the soil from being absorbed by the rain...
But calla, the 1983 flood long forgotten the moratorium on construction in Euskal Herria.
Klima aldaketaren eraginez, munduko lurralde gero eta gehiago idortzen ari dira, milioika pertsonaren jarduera eta bizimoduak kolokan ezarririk. Fenomeno horren frontean dago India erdialdeko Maharashtra estatua, non klimaren berotzeari eta lehortzeari metatu zaizkien oihan... [+]
Today’s Venice is built on an archipelago of 118 islands. These islands are connected by 455 bridges. The city is based on mud rather than Lura. Millions of trees in the area were cut down from the 9th century onwards to build piles and cement the city. Years have passed and... [+]
Lurrak guri zuhaitzak eman, eta guk lurrari egurra. Egungo bizimoldea bideraezina dela ikusita, Suitzako Alderdi Berdearen gazte adarrak galdeketara deitu ditu herritarrak, “garapen” ekonomikoa planetaren mugen gainetik jarri ala ez erabakitzeko. Izan ere, mundu... [+]
Eskola inguruko natur guneak aztertu dituzte Hernaniko Lehen Hezkuntzako bost ikastetxeetako ikasleek. Helburua, bikoitza: klima larrialdiari aurre egiteko eremu horiek identifikatu eta kontserbatzea batetik, eta hezkuntzarako erabiltzea, bestetik. Eskola bakoitzak natur eremu... [+]
Agintari gutxik aitortzen dute publikoki, disimulurik eta konplexurik gabe, multinazional kutsatzaileen alde daudela. Nahiago izaten dute enpresa horien aurpegi berdea babestu, “planetaren alde” lan egiten ari direla harro azpimarratu, eta kutsadura eta marroiz... [+]
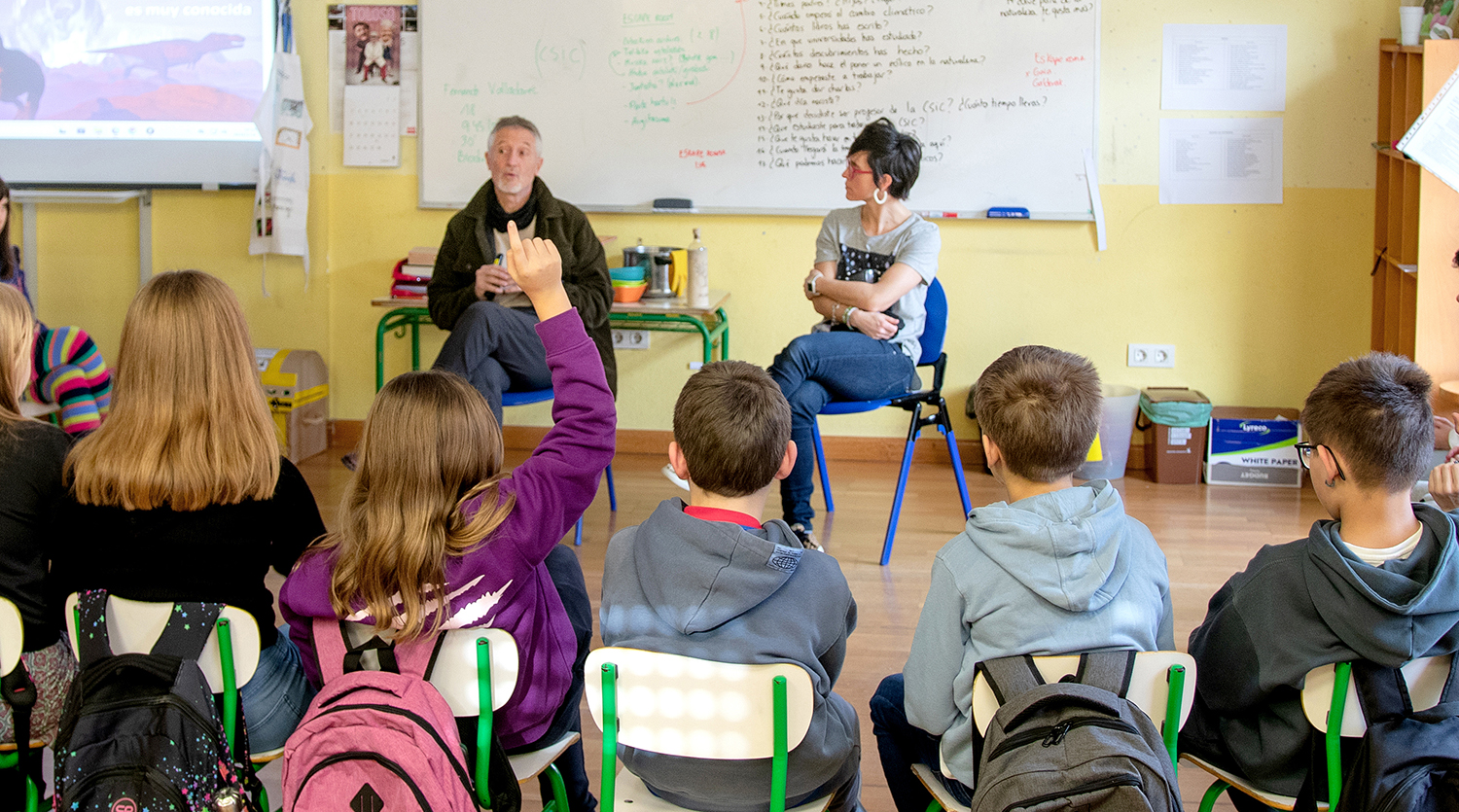
Biologian doktorea, CESIC Zientzia Ikerketen Kontseilu Nagusiko ikerlaria eta Madrilgo Rey Juan Carlos unibertsitateko irakaslea, Fernando Valladares (Mar del Plata, 1965) klima aldaketa eta ingurumen gaietan Espainiako Estatuko ahots kritiko ezagunenetako bat da. Urteak... [+]
Nola azaldu 10-12 urteko ikasleei bioaniztasunaren galerak eta klima aldaketaren ondorioek duten larritasuna, “ez dago ezer egiterik” ideia alboratu eta planetaren alde elkarrekin zer egin dezakegun gogoetatzeko? Fernando Valladares biologoak hainbat gako eman dizkie... [+]
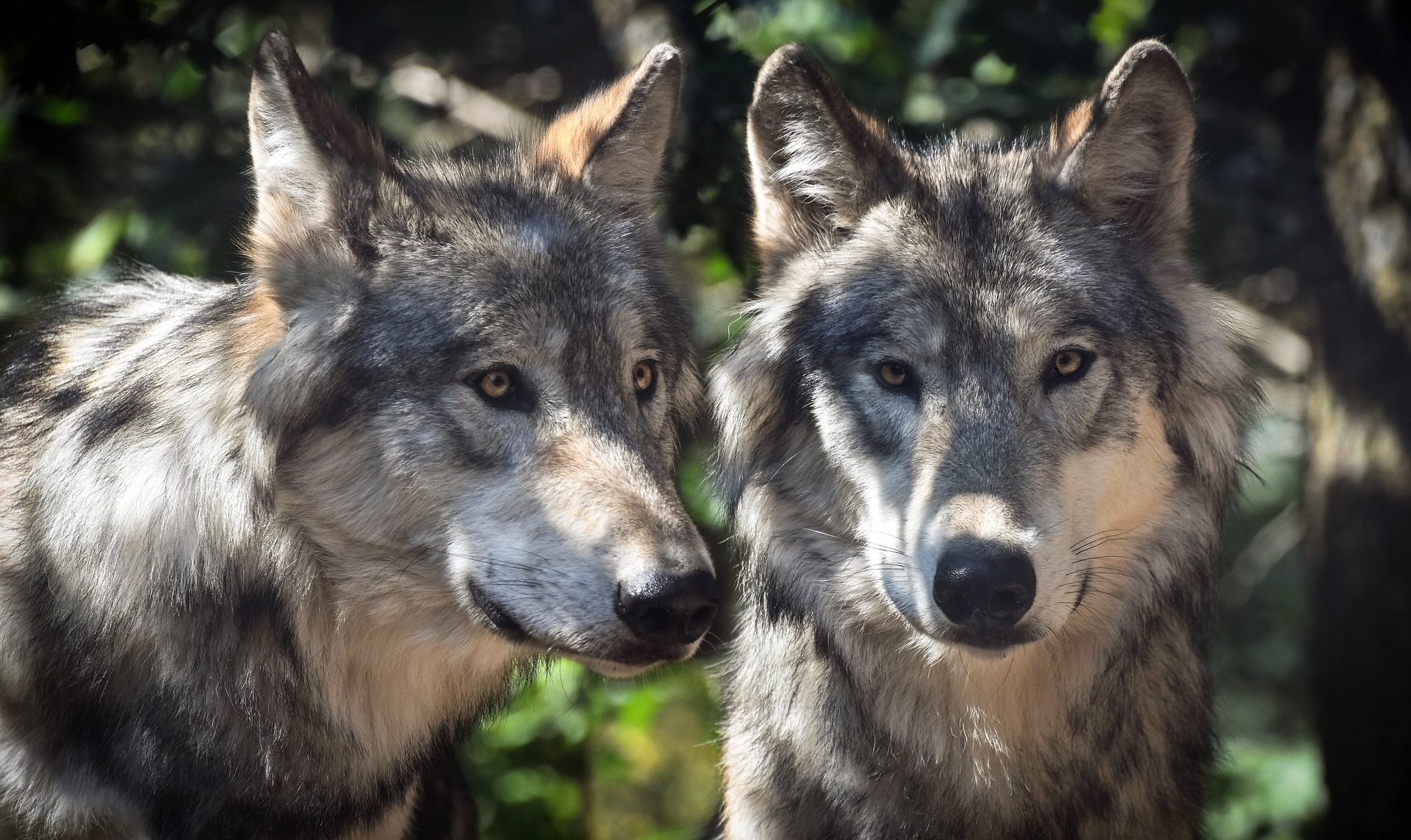
Eskoziako Lur Garaietara otsoak itzularazteak basoak bere onera ekartzen lagunduko lukeela adierazi dute Leeds unibertsitateko ikertzaileek.. Horrek, era berean, klima-larrialdiari aurre egiteko balioko lukeela baieztatu dute, basoek atmosferako karbono-dioxidoa xurgatuko... [+]

















_Glaciar.png)
