The sea is exhausted but wants to revive as in the Conil de la Frontera andaluz, in Lyme Bayen, England
- In Andalusia, 65,000 hectares of the Conil de la Frontera coast, fishermen and ecologists try to limit fishing in waters to revitalize a sea that is running out of fish or underwater vegetation, but owners of yachts and small boats dedicated to recreational fishing oppose. If the plan goes ahead, it can be repeated in Conil what Lyme Bayen demonstrated in England that the sea landed to the end has a small chance to demonstrate its desire for life.

The caravan composed of more than one hundred cars collapsed on 21 March the center of the city of Cadiz, in protest against the marine reserve of Mar de Gades, which the Government of Spain wants to establish in its surroundings. They claimed the right to continue fishing for their yachts, canoes and boats for leisure. At the moment, the new enemies have emerged from the fish that have been destroyed by the industrial fleet until they have almost disappeared.
Gades is the name that the Romans have today given to Gaditan, formerly called Gadir for Phoenicians. And they named Mar de Gades the reserve project prepared by environmentalists and artisanal fishing professionals, who meet fundamentally in the brotherhood of Conil de la Frontera, for many years: 35 kilometres of coastline near the Cadiz capital, from Sancti Petri to the tip of Trafalgar, with 12 miles in Spain, 65,000 hectares of sea, where drastic fishing will remain regulada.Prohibicion total fishing in the three determined areas of the interior.
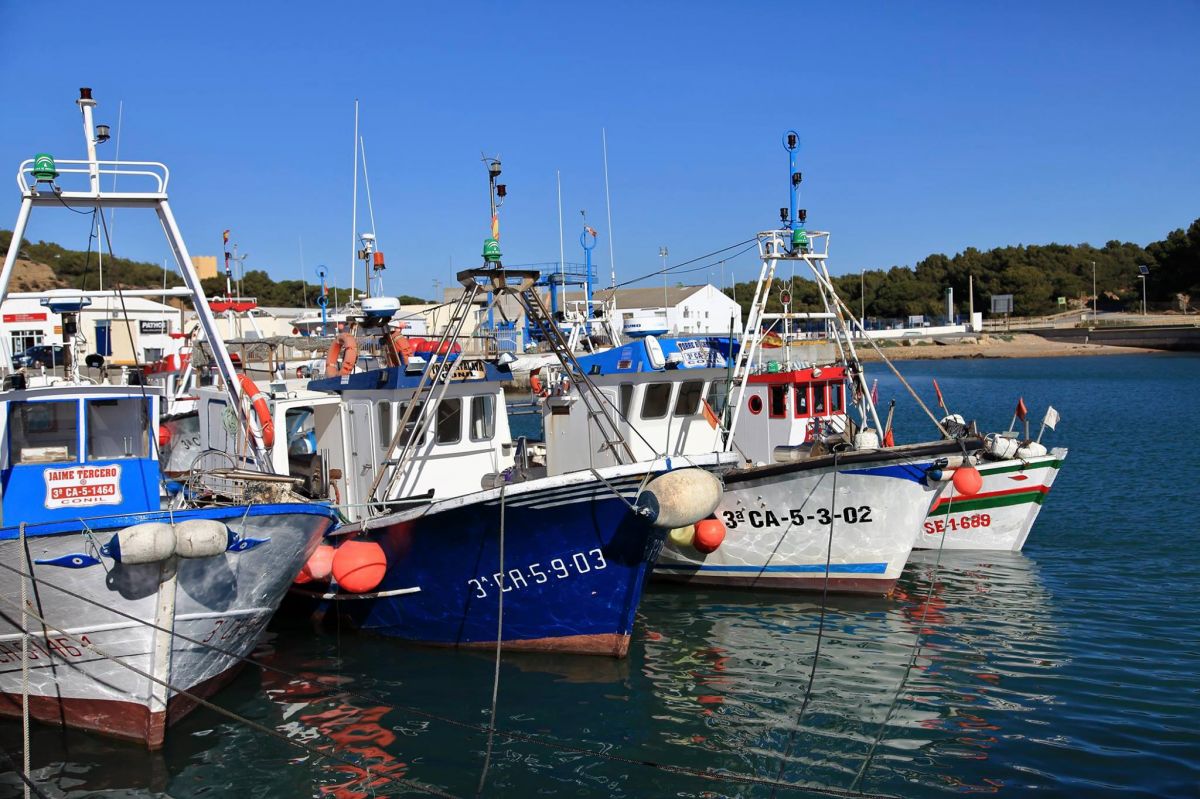

The port of Conil has 54 professional vapours, with about 200 jobs. The brotherhood that represents these small fishermen began to work in 20o9 the idea of booking based on the models that exist in the USA and Europe. Environmentalists in Action (Ekologistak Martxan, Hego Euskal Herria) helped define the limits of the reserve and its management proposals. However, the intention did not advance in the offices of the Spanish Administration and it was necessary for the World Nature Fund (WWF), a powerful non-governmental organization, to open its doors to politicians and bureaucrats. Finally, last February the Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food of Madrid gave access to the project and opened the deadline for interested parties to make representations.
Then the abovementioned amateur leisure fishermen have been mobilized, many in this hyper-tourist area: Sancti Petri, Chiclana, Barbate, Conil… 1,670 pastime vessels, large and small. In the anti-Reserve association there are 4,000 people, 20,000 signatures have been collected. It has not been known that the great steamships dedicated to industrial fishing have said anything, probably because they are occupied in other richer fisheries in the Mediterranean by the protection measures to which the European Union refers.
The promoters of the Gades Sea Reserve believe that unfished protected areas will allow the reproduction of diminished fish in recent decades and that prosperity will thus extend to the whole environment. In addition to fish, shellfish and molluscs, it is expected to save and recover the destruction of the seabed plants and corals, including the orange color of the coral Astroides calycularis. To this end, it is intended to divert large trawls from these 65,000 hectares, but it is also necessary to rigorously control fishing on the pretext of leisure, including the most furtive submarine.
Will the ministry of Madrid be able to maintain the tourism industry and the pressure of the pseudo-fishermen of pastimes? This brings forward the promoters of Sea de Gades who will have to gather more support in favour of the reserve: “Marine reserves are decided by consensus.” It's not the best sign.

News related to biodiversity often has little impact on the inlives of the planet's seas. Whales and other mammals, on the one hand, fish, on the other, have decreased dramatically in number and have decreased in size. These are the consequences of hunting and fishing carried out by man, among them the Basques condemn the destruction of a species of whale, which Callum Roberts has exposed in the intense book "The Unnatural History of the Sea", as well as in other books and films.
It can serve to comfort the grief of the disaster, but also to maintain the hope necessary to fight, both the seizure and the longing and the strength to revitalize the sea in the shelters. For example, in the Lyme Bay Maritime Park (England).
In southwestern England, in the vicinity of Plymouth, the marine mantle around Lyme Bay is also known as Jurassic Coast, due to the peculiar footprints that paleontologists have found. It is an area of great biodiversity, with very unique species at its bottom, both vegetables and corals, as well as very rich in fish. In the 1990s, ecologists reinforced the protection campaigns of the area.
Lyme Bay shells, including vieira or pilgrim shells, have always been known. Crabs excavating the seabed, with metal garbage carried, are collected, but until 1980 the equipment used by local fishermen had only the strength to explore the sand. Scallops were reduced and technology was advancing, as by the 1990s the bottom of the bay was not leaving coral or plant, as the images flooded by ecologists showed. 2005.erako, in addition, large vapours from other English ports came to Bieiras to dig even more Lyme Bay funds.
In 2008, in view of the seriousness of the situation, the London Government finally declared the protection of the Lyme Bay area, banning excavations with dredges and other crabs on 16,000 hectares, which today has 23,000 strictly regulated hectares. But since it is easier to ban an activity than to organise alternative management, the people involved in Lyme Bay have had to walk a path full of friction until they reach the balance that they have today.
In addition to the government and local authorities, the environmental organization Blue Marine Foundation and the fishermen and officers of Lyme Bay have taken part in organizing the new march of the Fisheries and Conservation Reserve. The documentary 'Lyme Bay' shows the journey and the current situation of this burrow: recovery. The scientists who speak there acknowledge that in the years after the establishment of the reserve they were very pessimistic, as the seabed followed a rock in the form of a desert, but from the fourth year the change began to materialize as a miracle, with the attention and proliferation of new plants and corals, with the proliferation of shells, shellfish and fish in these waters and the irradiation of the new life to the nearby waters.