We took the house off the abyss.
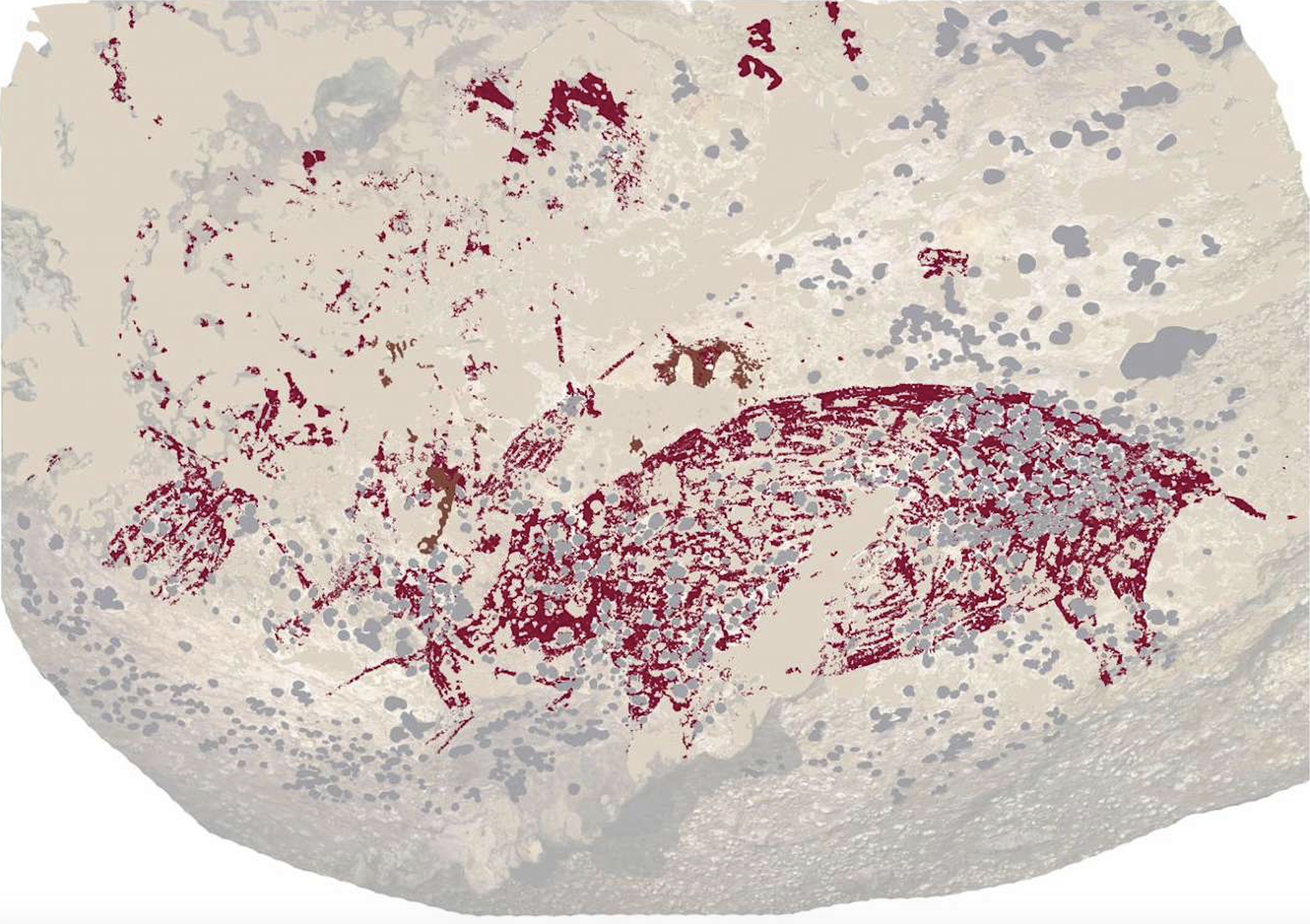
- In a cave of Amoroto are the marks of the claws of a cavernary bear. The main hypothesis about why the species has been extinct so far has been climate, but recent studies conclude that mitochondrial DNA began to fall into the caves about 50,000 years ago, before climate change. That's why they've linked the extinction of these bears to the spread of our species.

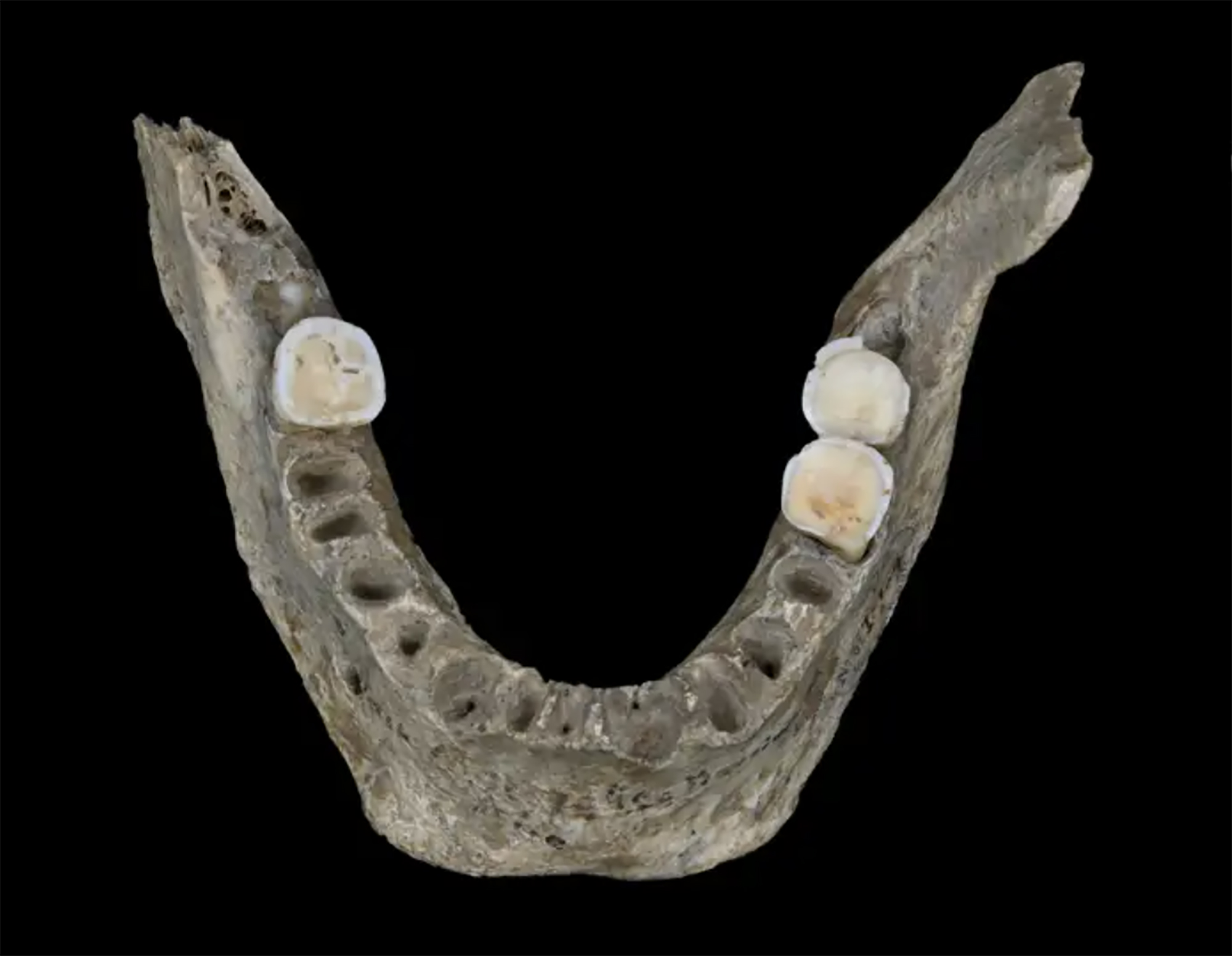
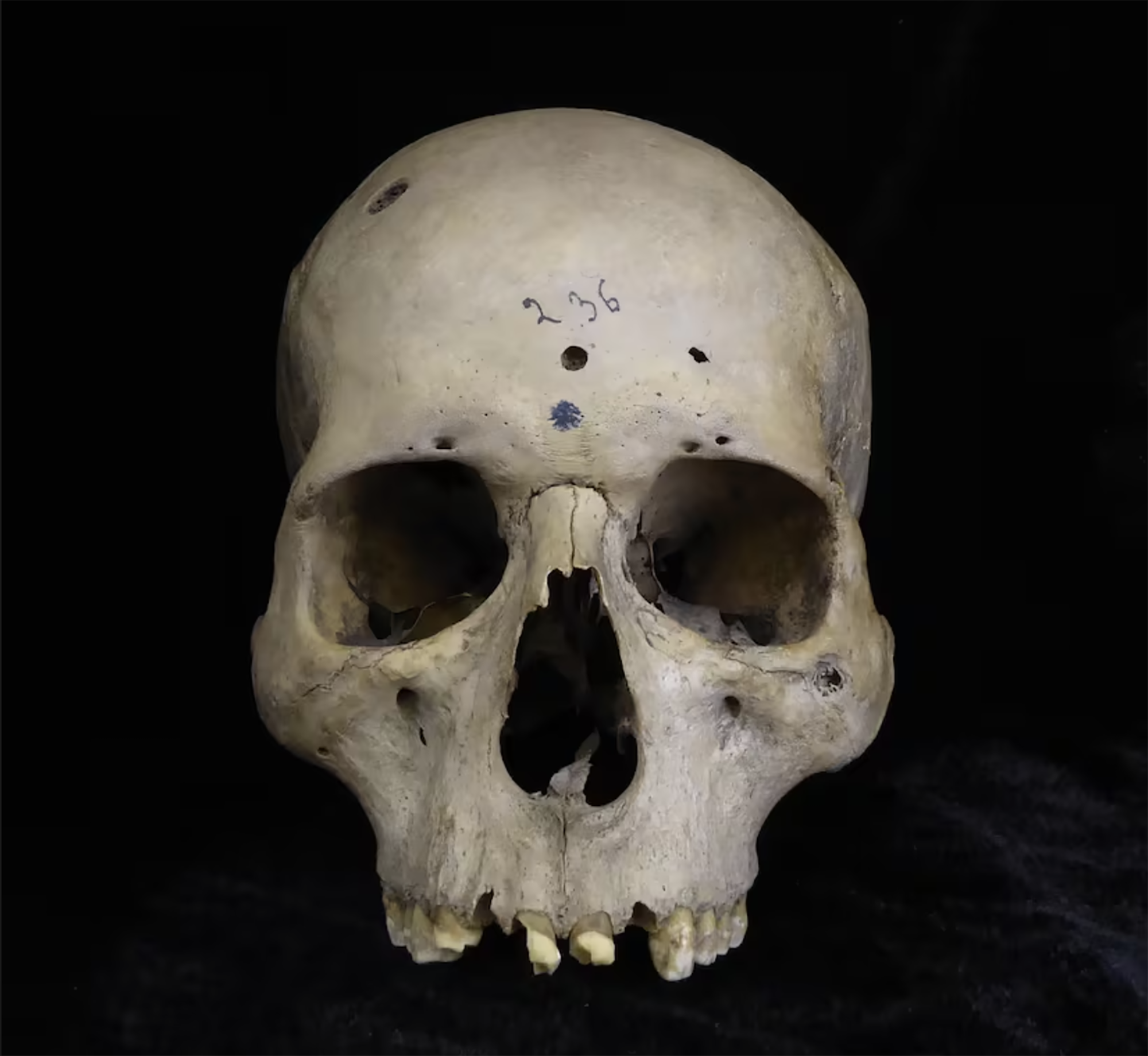
Amoroto, over 24,000 years ago. A cave bear left marks of his claw in a cave. Recently, the speleological association Ades has discovered this cave, catalogued with the code MG-12. In addition to the mark of the bear, in the cave they have also found a human skull, although they have not yet been evaluated and dated by the agents. But we know that the fingerprints of the vertex are over 24000-26,000 years, since at that time the species Ursus spelaeus was extinct.
Until the last decade, the main hypothesis about the cause of the extinction of caves has been the climate, which means that they did not withstand the last glacier and disappeared. However, as several experts have warned, the simas survived the previous glaciations. Another hypothesis is that the species was destroyed by a low diet. However, the study of some bones found in Romania in 2008 showed that the diet of caves was more varied than was thought.
Two years later, in 2010, chaired by the Max Planck Institute, a group of international scientists conducted a study that blamed man for abandoning climate or food. Recently, the mitochondrial DNA of 17 remains found in Siberia, Ukraine and Galicia has been analyzed and it has been concluded that the fall of the caves began some 50,000 years ago, before climate change. That's why they've linked the extinction of these bears to the spread of our species.
Parietal bears are rarely depicted in hunting scenes among the buttresses of the time – brown bears are much more frequent – and the trace of bears found in the caves along with human remains are related to rituals. All this indicates that the simas were of great ritual importance for humans of the time, but that they were not hunted. Humans did not directly kill bears. But they left them with no space to hibernate. As Homo sapiens expanded, more and more caves were occupied as a place of residence. Brown bears have the ability to hibernate out of the caves, protected by vegetation, but simas don't. Some were unable to enter the caves they used before, and others were unable to spend the winter outside; others found inadequate caves, too deep and failed to survive in the spring.
Pending the investigation of the remains found in Amoroto, remains of caves and humans have been found in other caves in recent years, and this hypothesis is becoming stronger.
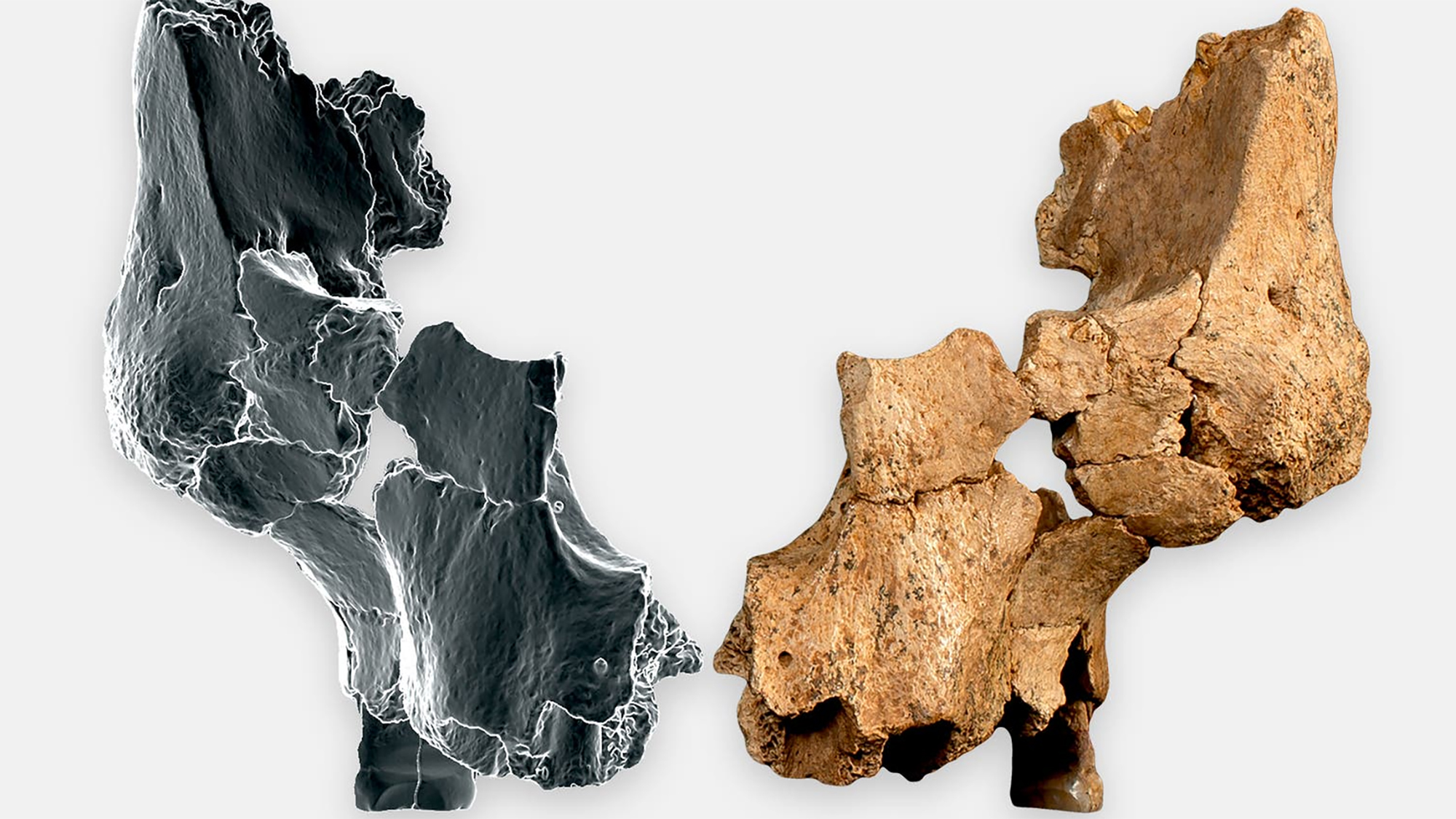
Atapuercako aztarnategian hominido zahar baten aurpegi-hezur zatiak aurkitu dituzte. Homo affinis erectus bezala sailkatu dute giza-espezieen artean, eta gure arbasoek Afrikatik kanpora egindako lehen migrazioei buruzko teoriak irauli ditzake, adituen arabera.
In the Maszycka cave in Poland, remains of 18,000 years ago were found at the end of the 19th century. But recently, human bones have been studied using new technologies and found clear signs of cannibalism.
This is not the first time that a study has reached this conclusion,... [+]
Archaeologists have discovered more than 600 engraved stones at the Vasagård site in Denmark. According to the results of the data, dating back to 4,900 years ago, it is also known that a violent eruption of a volcano occurred in Alaska at that time. The effects of this... [+]
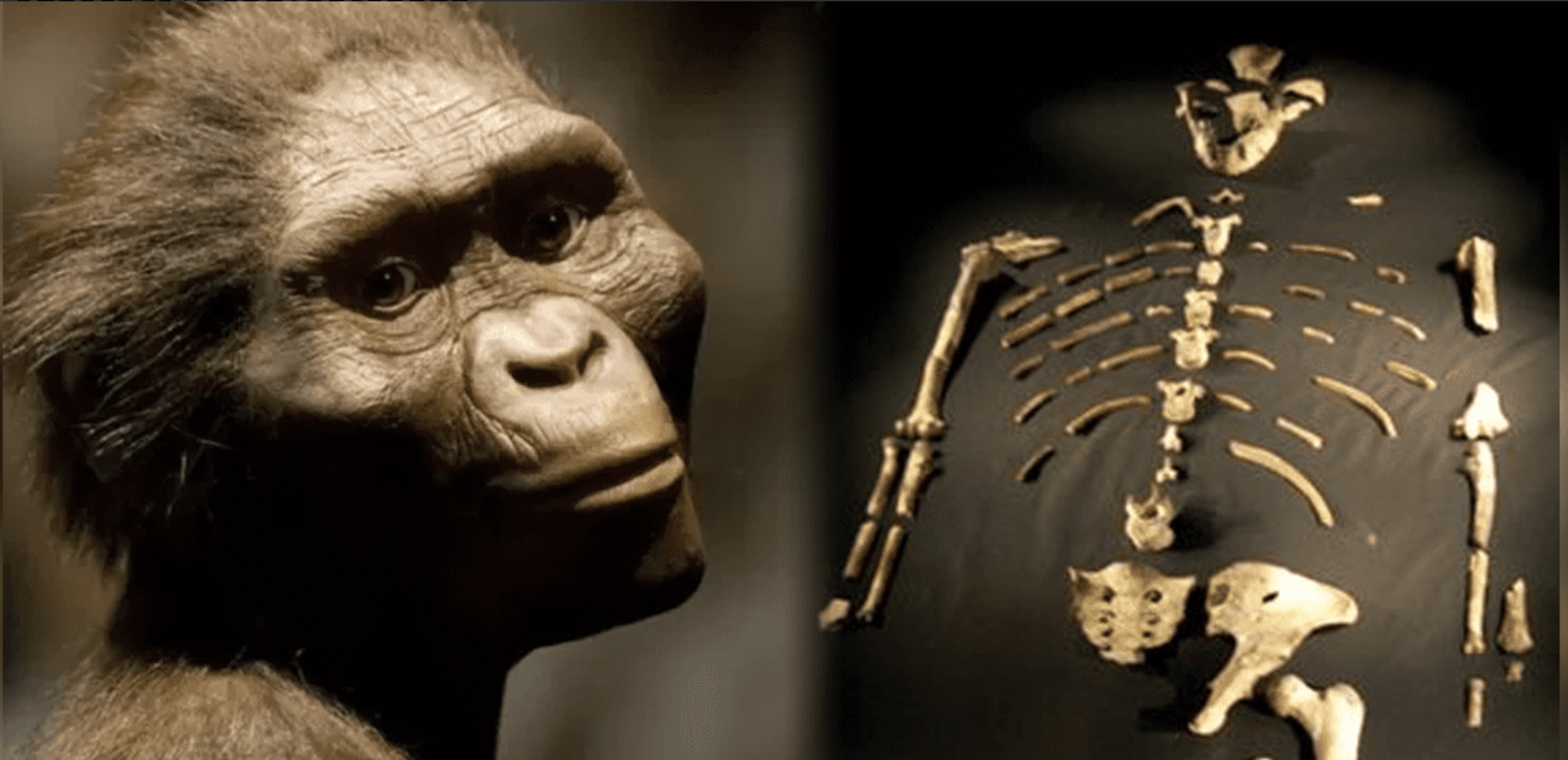
Ethiopia, 24 November 1974. Lucy's skeleton was found in Hadar, one of the oldest traces of human ancestors. The Australian hominid of Australopithecus afarensis is between 3.2 and 3.5 million years old.
So they considered it the ancestor of species, the mother of all of us. In... [+]
A group of archaeologists from the University of Berkeley, California, USA. That is, men didn't launch the lances to hunt mammoths and other great mammals. That was the most widespread hypothesis so far, the technique we've seen in movies, video games ...
But the study, published... [+]
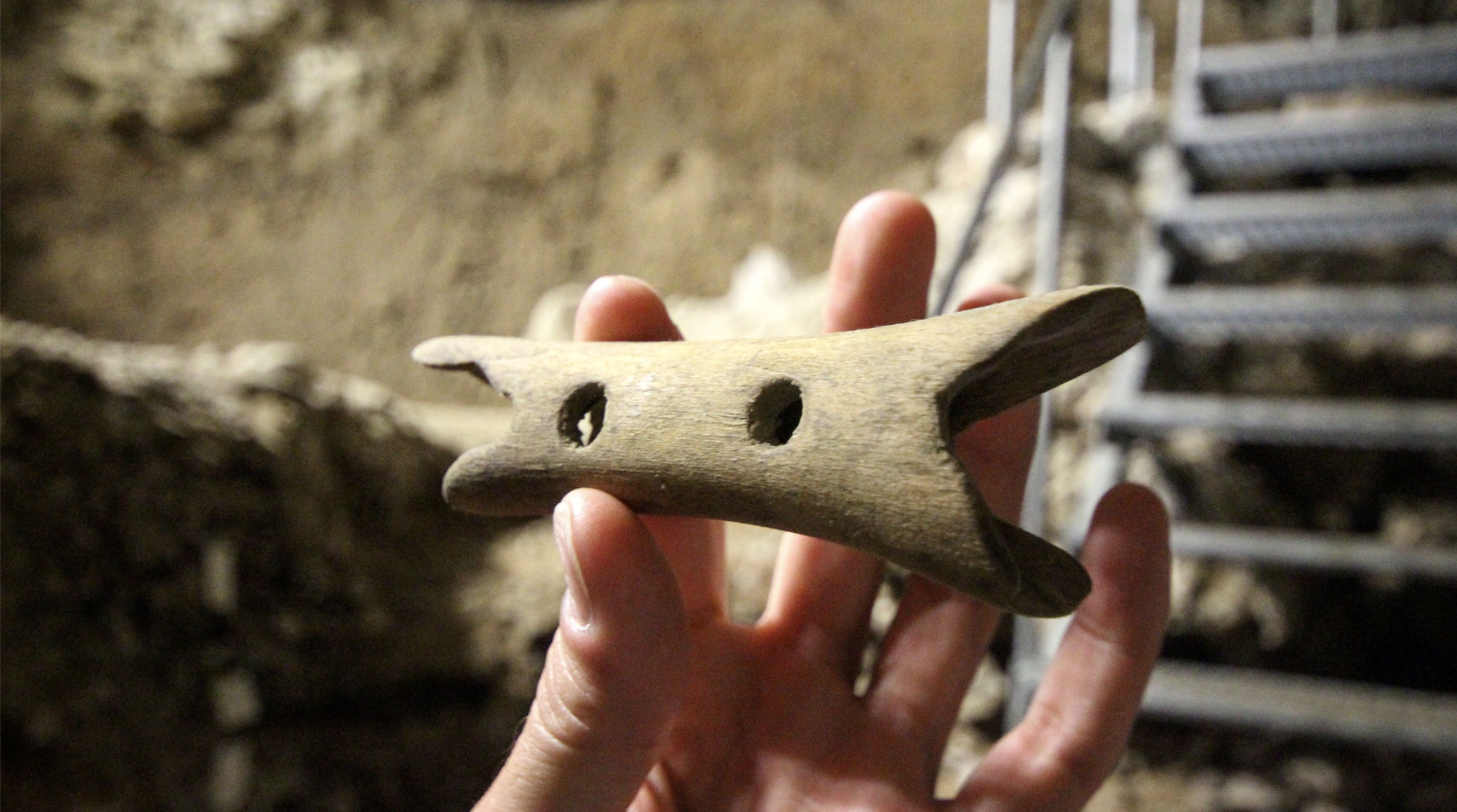
Geissenkloesterle (Germany), 42,000 years ago. Those living in the cave of the Danube basin made a flute with bird bones and mammoth ivory. At the same time, the inhabitants of the cave of Divje Babe in Slovenia also made a flute with the femur of a bear. These are the oldest... [+]
In the south of the Indonesian island of Sulawesi, in the cave of Leang Karampuang, archaeologists from the Griffith and Southern Cross universities and the Indonesian National Agency have discovered a painting of three anthropomorphic figures and a boar. According to the study... [+]
Two years ago, the Catalan archaeologist Edgard Camarós, two human skulls and Cancer? He found a motif card inside a cardboard box at Cambridge University. Skulls were coming from Giga, from Egypt, and he recently published in the journal Frontiers in Medicine, his team has... [+]
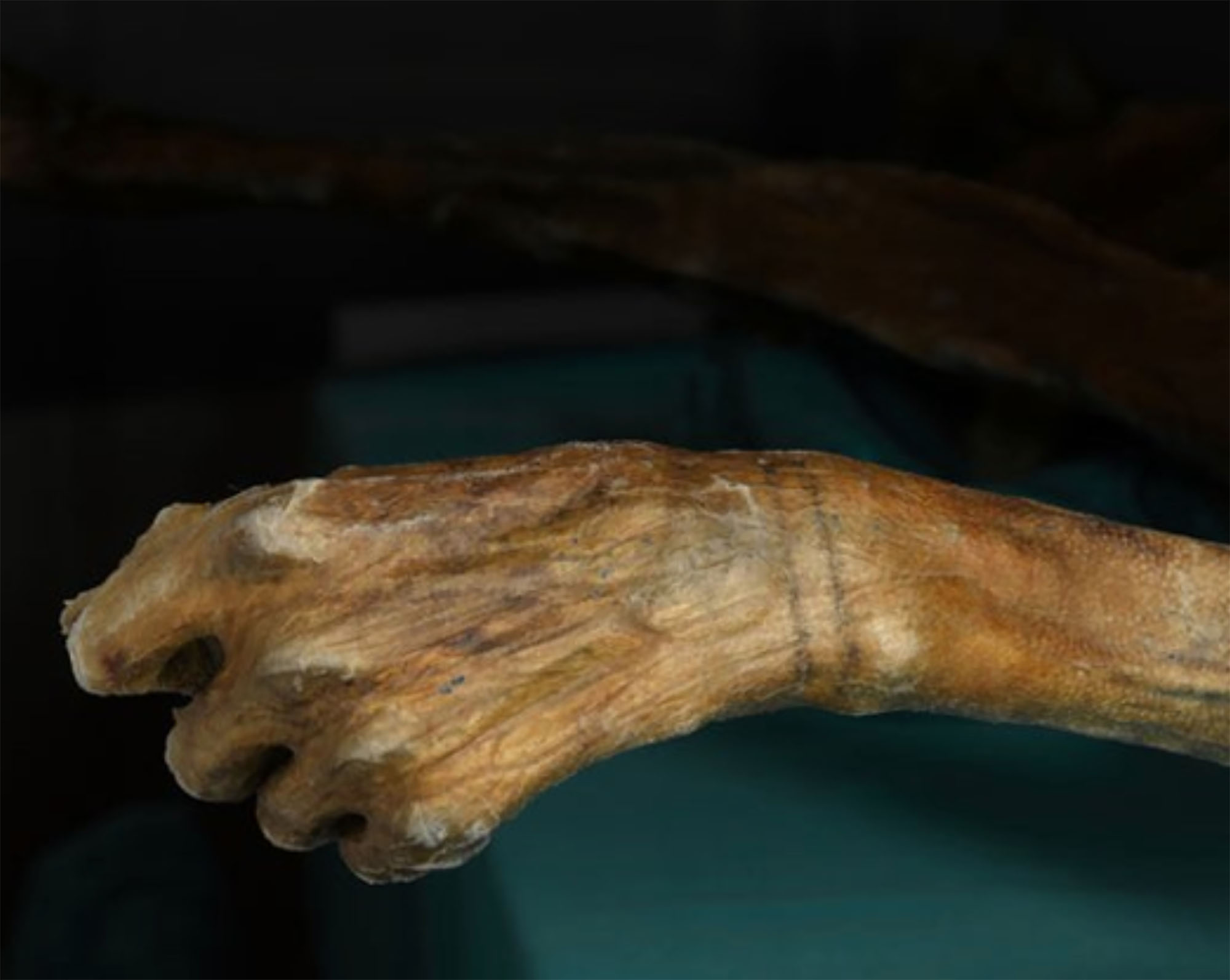
Since they discovered the corpse of Ötzi in the Alps in 1991, the 5,000 years preserved in very good condition have been used for numerous investigations. From the beginning, the 61 tattoos he had on his skin were the ones that cared for him. Experts believed these tattoos were... [+]
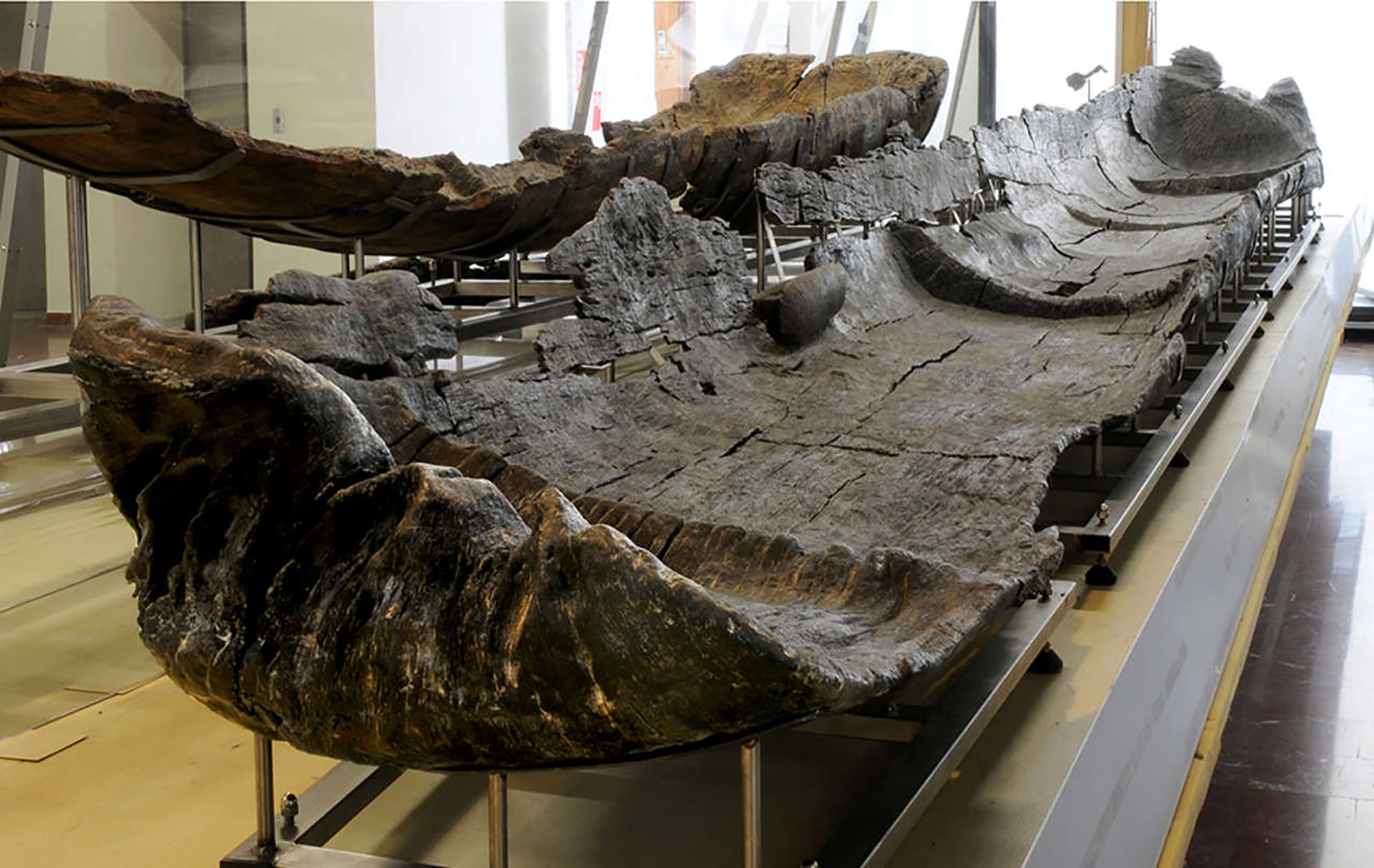
Between 1992 and 2006, in the waters of Lake Bracciano of Rome, the site of La Marmotta del Neolitico was excavated early. They recently published in Plos One magazine a study on the five piraguas found there. It is estimated that the boats are between 7,000-7,500 years... [+]
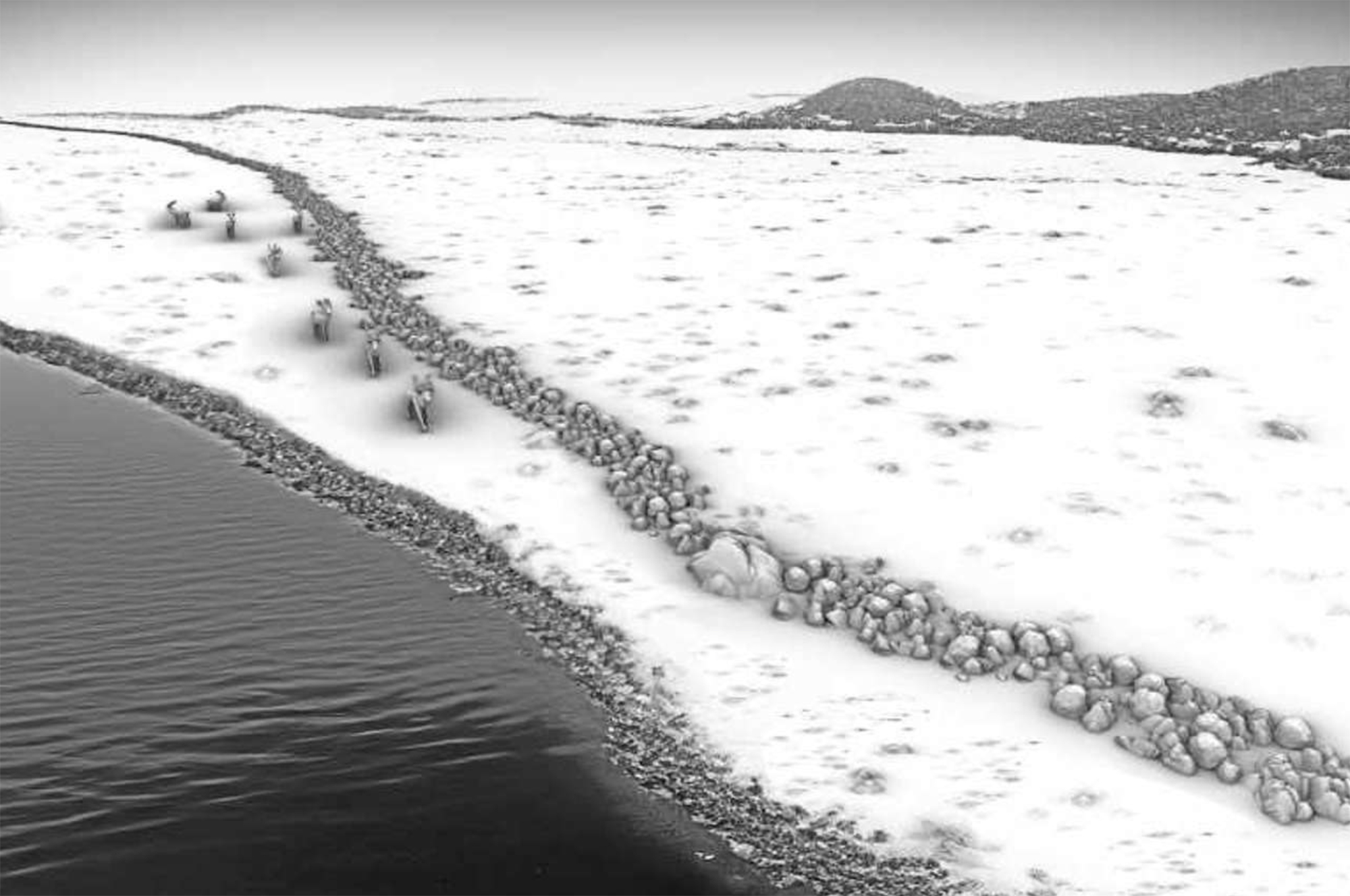
In the Gulf of Mecklenburg, in Baltic waters, archaeologists identified in 2021 a stone structure of almost a kilometre. Now a team of interdisciplinary researchers has published a study on the wall in the journal PNAS.
The structure is about 10,000 years old and has come to... [+]