"The sexual crimes committed by white men against Indian women go unpunished"
- Edward Chu (Santa Rosa de California, EE.UU. 1974) is a doctor and anthropologist who serves the Navajo Indians in the hospital of Tuba City, Arizona, through the Regional Health Care Corporation. Weave your work by uniting the social view and the clinical vision.
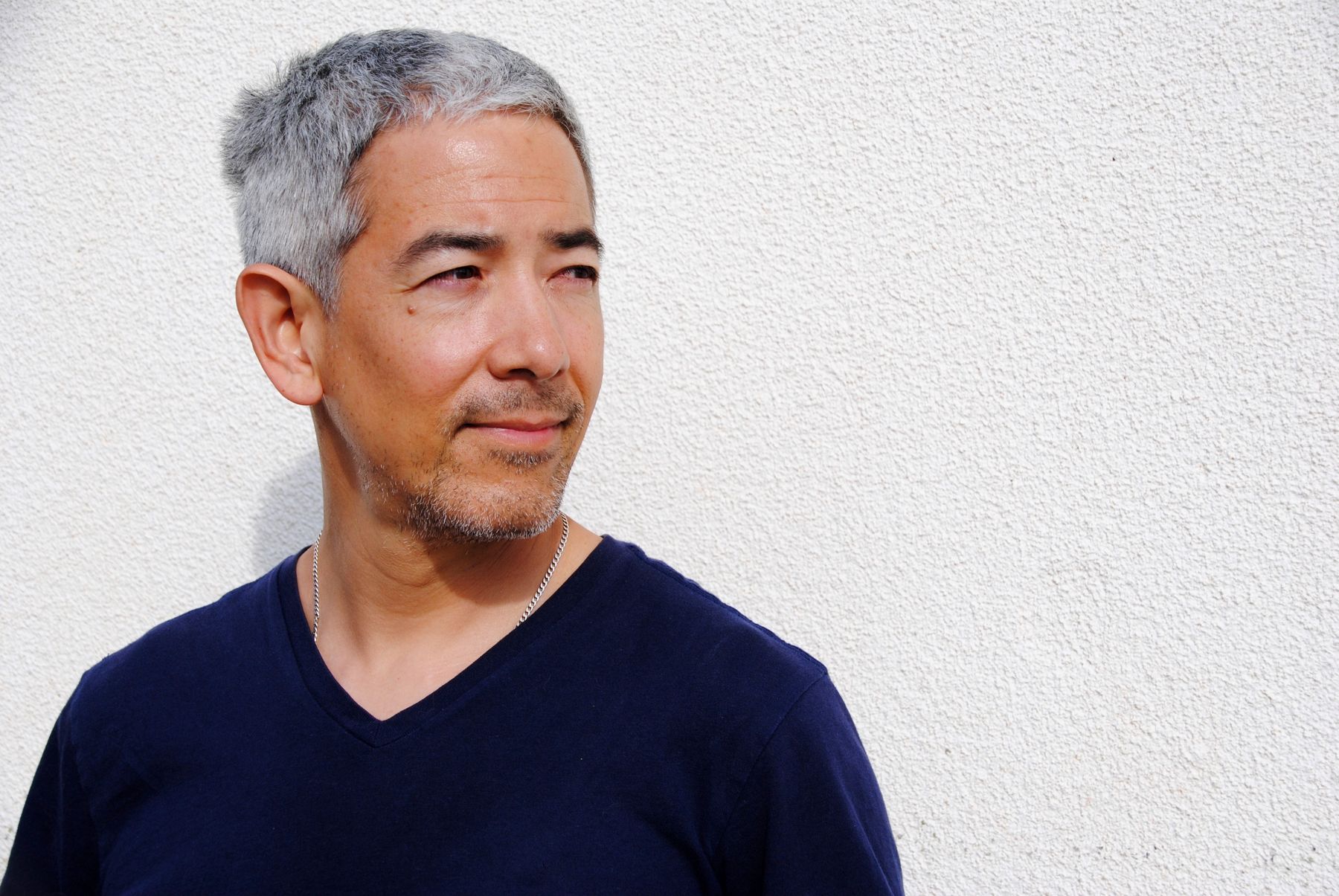

You grew up and learned between Connecticut, Boston and Baltimore. But at nearly 3,500 kilometers, at the other end of the United States, you've decided to work in the middle of the Arizona Desert, the largest enclave in the nation of Navajo. Why? The
U.S. health system, in addition to the population, is extremely frustrating for the professionals we want to make social medicine. The practice of a Amerindian reservation, however, gives us every day keys to understanding the impact of socioeconomic conditions on the health of citizens. It is a suitable place to influence community health.
Why do you say that the system for doctors too is nasty?
Imagine you're working in the emergency room, you're able to stabilize a patient who's come in the middle of a diabetes crisis and send him home. He knows he'll be admitted again in a few days' time, because he doesn't have money to pay for insulin treatment, because he doesn't have insurance or because the insurance he pays doesn't include it.
What access to health do hometowns have compared to the rest of the U.S. population? United States
They are privileged compared to Americans living in similar socio-economic situations, at least if they can prove that they reside within the reserve and belong to a tribe of origin, because they are exempt from paying for a medical service. Of course, the privilege is relative, because the budget estimated by the Federal Government for each of these native Indians does not amount to half the amount that a normal American citizen with private insurance invests in it and therefore receives a very basic service. But, in turn, and bearing in mind that in Tuba City, for example, the unemployment rate is 50%, if not for that exception, the majority of the population would not have any coverage. The situation is now much worse for immigrants who do not have nationality.
Why?In 2015,
Obama made health insurance coverage mandatory for all citizens, and that reform established the minimum services to include. It also set in motion a comprehensive system of financial aid for citizens who could not afford these minima. The media campaign did not tell, but the money for this aid was until then spent on NGOs and public charitable clinics, so the non-citizen immigrants who benefited from them have been left unprotected.
Is there any other limitation that directly affects Navajo and other tribes of origin?The new aid
system linked to the Obama reform suddenly brought hundreds of thousands of patients into the health system. On the contrary, we will need at least eight years to train new doctors and nurses and add them to the system. As a result, many patients who have managed to overcome the economic barrier still do not receive adequate care, precisely because of the lack of professionals.

But why does this affect Indians more than other citizens?
Well, in general, it affects all the people who live in rural areas far from major cities, where the shortage of human resources, ambulances and other material resources is even more serious. But the Indians live more isolated than anyone, in the areas that the Federal Government granted to the primitive tribes, that is, reservations, because in most cases they are not in their own domain, but in poor, sterile and undeveloped areas, which were not of great interest to the Government. They were displaced to areas of poor accessibility, far from urban centers and, therefore, from the health system.
What are the most common pathologies in the Tuba City Reserve and what relationship do they have with the life of the Navajo?Most serious diseases are related to alcoholism, sedentarism and unemployment obesity: diabetes, mainly
liver and cardiovascular diseases. It mainly affects generations from 20 to 40 years, as older people maintain a traditional diet and, in general, make a more active life, have maintained the responsibility of searching for water or going to search for wood. On the other hand, the degree of violence is extremely high in the reserve, as almost all families have lost a member, and these killings occur between familiar people, especially between friends, brothers or cousins, and also between couples, in both ways. They drink together, get drunk and end up fighting.
“Most serious diseases are related to alcoholism, sedentarism and unemployment obesity: diabetes, mainly liver and cardiovascular diseases”
Is sexual violence also common?
Yes. At the age of fifteen, when girls start to leave at night, they start to be victims of rape. The aggressors are often white men who are out of the reserve. The laws adopted by the Government of Navajo apply only to Navajo persons and, at the same time, the federal penal code cannot sanction crimes that occurred within the jurisdiction of the Government of Navajo. Therefore, the sexual crimes committed by white men on the Indian and against Indian women go unpunished in a legal limbo.
A fairly widespread belief in the United States states states that alcohol has a faster and greater effect on the Indians, and that for the same genetic reason they have a greater predisposition to dependence.
Yes, it is a very widespread conviction. But years of experience have taught me that this is a socio-economic, non-cultural problem, and that white Americans living in similar conditions also resort to alcohol and drugs as a balm against frustration. The fact is that the Government moved the tribes of origin to particularly hard areas, in many cases in the middle of the desert. In Tuba City, for example, there is only one supermarket and a fast food restaurant. Two years ago a small film was opened, but children and adolescents have no other alternative for leisure.
And what do they live from?
Traditionally, agriculture and livestock have been the pillars of the Navajo economy. The land belongs to the Indian government, which is in charge of adapting some of the plots to each family. People who live on land with some source of water grow sheep, cattle, horses... and live quite well, without problems of alcoholism. But within the Indian Government there is also great corruption, so the division of land is based on favoritism and the exchange of favors. There is also a coal mine, but the number of jobs it offers is too small for a population of more than 8,500, so many join the army to not only collect salaries, but also education.
In 2014, the Federal Government signed a $554 million compensation agreement with the Government of Navajo for poor management of natural resources. What has happened to that money? This
is the largest historical economic compensation that the Government has made to an indigenous community. The Government of Navajo has allegedly paid for this. But it doesn't seem to have reached citizenship. Many families still live in unpaved houses without electricity or water, which has a direct impact on their hygiene, health and quality of life. They cannot clean wounds, for example. Or, for example, people who need a wheelchair or a wheelbarrow for walking can hardly move in the street or inside the house. On the other hand, although in daily life the Navajo do not smoke tobacco or anything, because they keep the cistern for special ceremonies, we serve many children and adults with other lung problems, who use firewood in the kitchen to warm the house or burn garbage.

The Sioux Nation rose in 2016 against the pipeline that Trump wants to build within the sacred lands of Standing Rock (North Dakota). Other tribes joined the protests and, in addition to paralyzing the project, managed to make the issue of Amerindians and their rights visible for the first time.
Yes. This initiative not only managed to involve the people of origin, but also environmentalists, politicians, veterans of war and even some Hollywood star. They stayed for a moment in the foreground, but quickly fell into oblivion. The vast majority of American citizens know nothing about the history, culture, rights or poor living conditions of their people of origin. They are a very small minority, no one mentions them in his political speech. Some sports teams use the image of the Indians as pets, and otherwise... they know them because they own casinos, because in the reserves casinos are legal.
What is the relationship between Western medicine and traditional Navajo medicine in the Tuba City Reserve?The Navajo people have quite
strongly preserved their culture, language, customs and even traditional medicine. Therefore, at the reserve hospital we have a space called Hogan – the name of the traditional Navajo houses is Hogan – in which the shamans of the tribe will celebrate their ceremonies if requested by any admitted patient. These are mainly rites and songs of reinsertion because the Navajo believe that diseases are the result of a disconnection or lack of balance between the patient and his environment. In these ceremonies, the whole family of the patient should normally participate, so the social component that does not take into account Western medicine is recognized as being of great importance. That is why, for example, to cure families that have been broken by alcoholism is often very useful. On the other hand, the hospital technicians are 100% Navajo, and also 50% of the nurses. In fact, the hospital is for them an important work alternative. Doctors, on the other hand, are still very few.