The first black with Canadian Basque
- North America, first years of the 17th century. Mathieu da Costa was the first free black person to reach the current east coast of Canada, according to the Canadian Heritage Institute.

We don't know where and when Da Costa was born and died. We know he was of African origin, he was an interpreter, and he worked for the French colonizers Pierre Dugua de Bots and Samuel de Champlain. It was said that it dominated French, Portuguese, Dutch and Euskera – in particular algonkin-Euskera pidgina – and, of course, that it was the mother tongue, although it was not known anywhere.
According to historians, Africans began to work as interpreters for the Portuguese at the end of the 15th century and a century later, as Europeans were increasingly explored in southern Africa, for the Dutch, French and English. Maybe that's why Da Costa spoke in French, Dutch and Portuguese.
But we don't know how Euskera Algonquin, the pidgin, was able to become an interpreter with the elders of the San Laurendi River. Because it was the main instrument of communication between Europeans and natives. The Basque whalers arrived around the 1520's to the surroundings of Newfoundland and Labrador and in their relations with the inhabitants a pidgina emerged with the words of micmakera, innera and Euskera, which also had some touches of gas, which would later be used by the French colonizers. Da Costa, perhaps, learned Euskera in Europe, or directly pidgina. Or maybe I'll study in North America itself, in active.
The African interpreter returned to Europe in February or March 1607, after a document revealed that the secretary of Mandela of Mons, Pierre Dugua, had come to Amsterdam to seek him. The Dutch reportedly captured several French boats and kidnapped Da Costa. It follows that he had already worked on the Canadian Atlantic coast. In 1608 Da Costa signed a contract with the Norwegian merchant Nicolas de Bauquemare to perform for three years the work of translator of “travel to Canada, Academy and any other place”. We do not know if he re-embarked, but at least he did not complete the whole contract. In December 1609, Mathieu Da Costa was imprisoned in Le Havre for an “act of shame.” And from then on there is no trace of him.
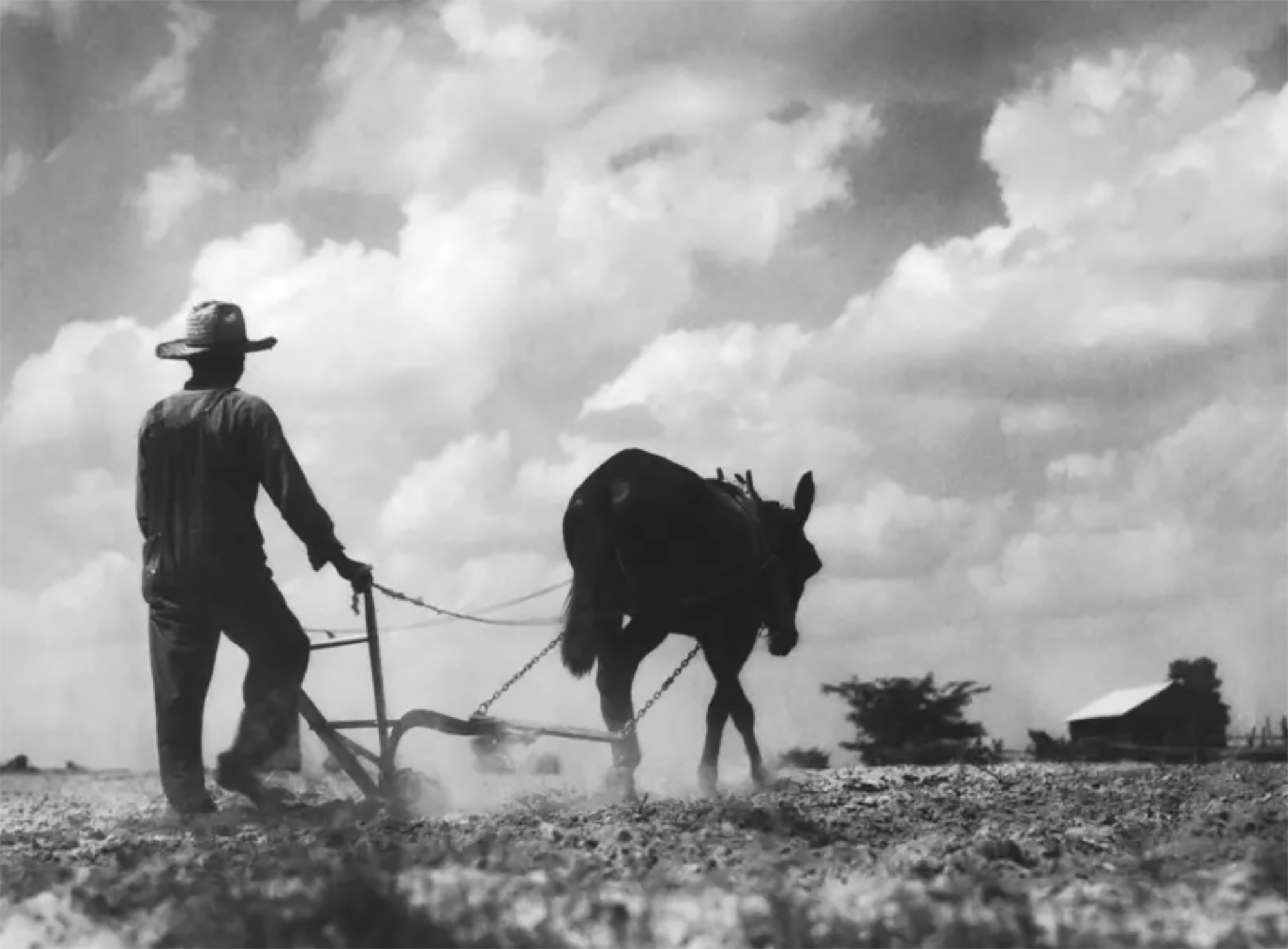
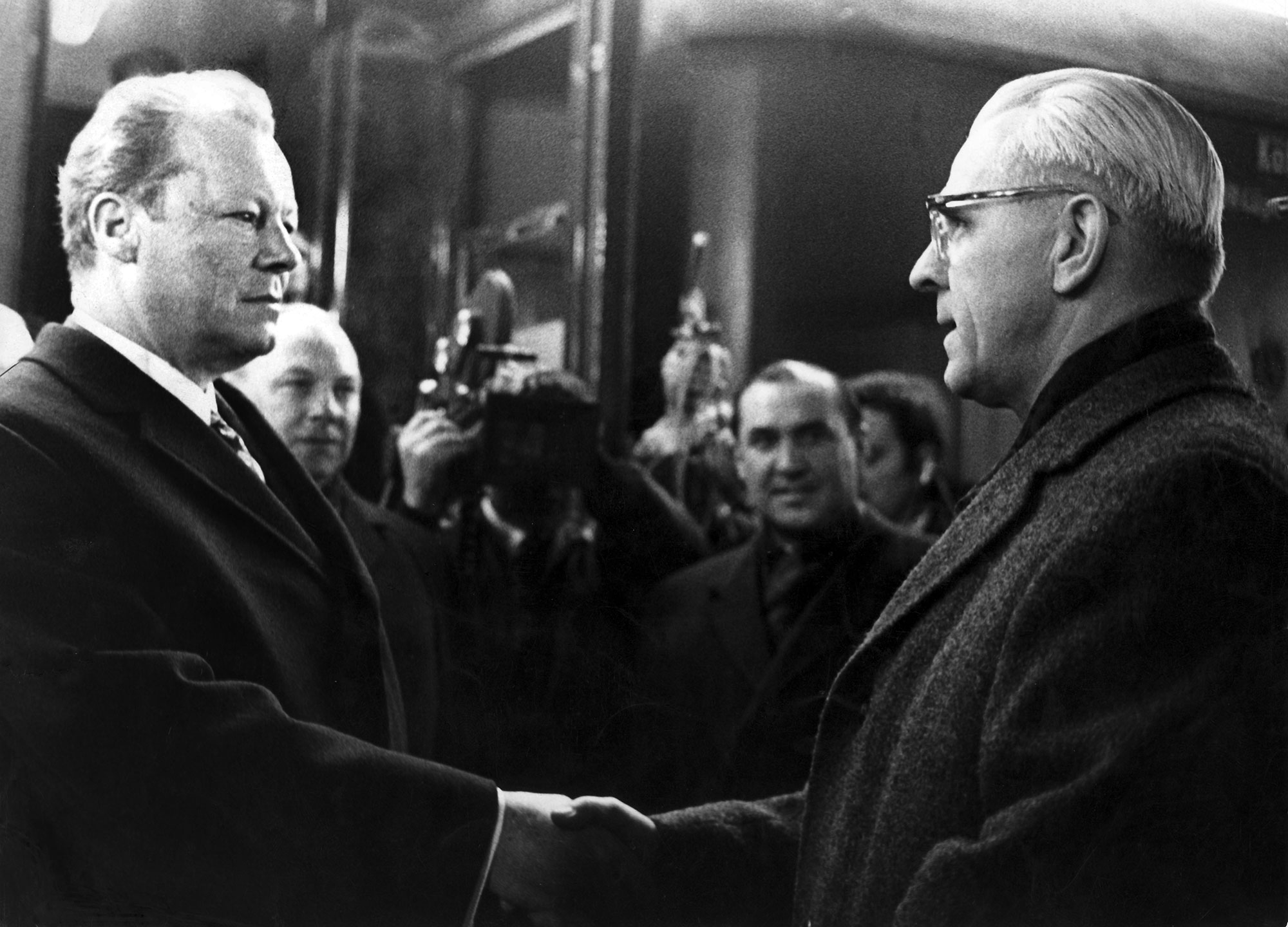
Washington, D.C., June 17, 1930. The U.S. Congress passed the Tariff Act. It is also known as the Smoot-Hawley Act because it was promoted by Senator Reed Smoot and Representative Willis Hawley.
The law raised import tax limits for about 900 products by 40% to 60% in order to... [+]
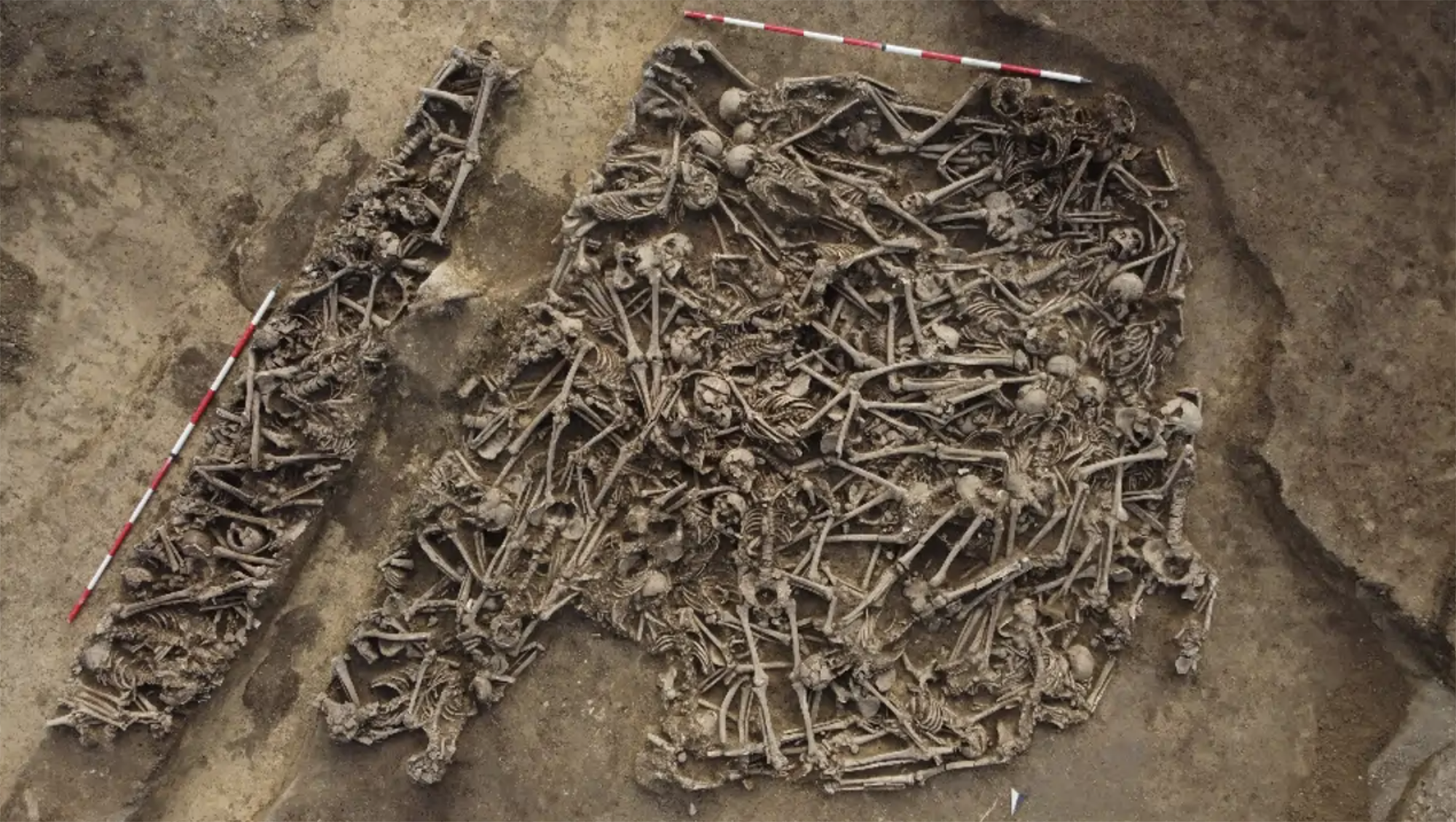
During the renovation of a sports field in the Simmering district of Vienna, a mass grave with 150 bodies was discovered in October 2024. They conclude that they were Roman legionnaires and A.D. They died around 100 years ago. Or rather, they were killed.
The bodies were buried... [+]
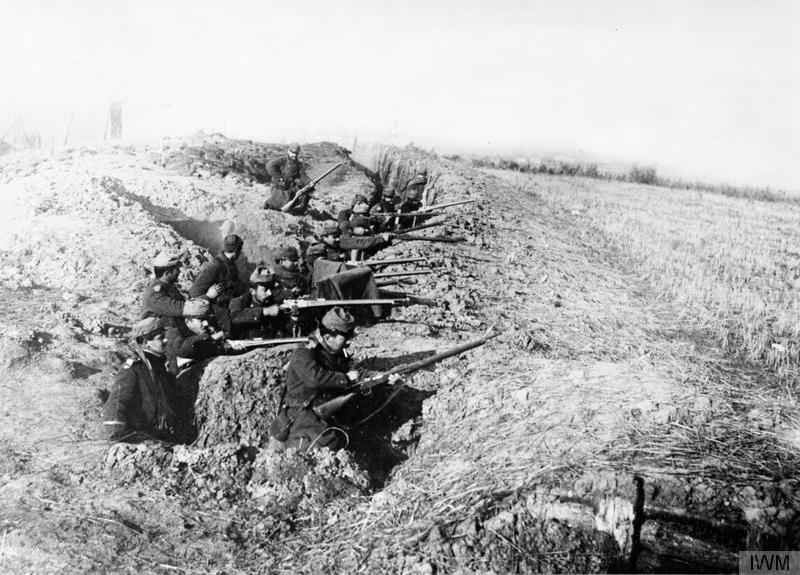
My mother always says: “I never understood why World War I happened. It doesn't make any sense to him. He does not understand why the old European powers were involved in such barbarism and does not get into his head how they were persuaded to kill these young men from Europe,... [+]
Until now we have believed that those in charge of copying books during the Middle Ages and before the printing press was opened were men, specifically monks of monasteries.
But a group of researchers from the University of Bergen, Norway, concludes that women also worked as... [+]
Florentzia, 1886. Carlo Collodi Le avventure de Pinocchio eleberri ezagunaren egileak zera idatzi zuen pizzari buruz: “Labean txigortutako ogi orea, gainean eskura dagoen edozer gauzaz egindako saltsa duena”. Pizza hark “zikinkeria konplexu tankera” zuela... [+]
Ereserkiek, kanta-modalitate zehatz, eder eta arriskutsu horiek, komunitate bati zuzentzea izan ohi dute helburu. “Ene aberri eta sasoiko lagunok”, hasten da Sarrionandiaren poema ezaguna. Ereserki bat da, jakina: horra nori zuzentzen zaion tonu solemnean, handitxo... [+]
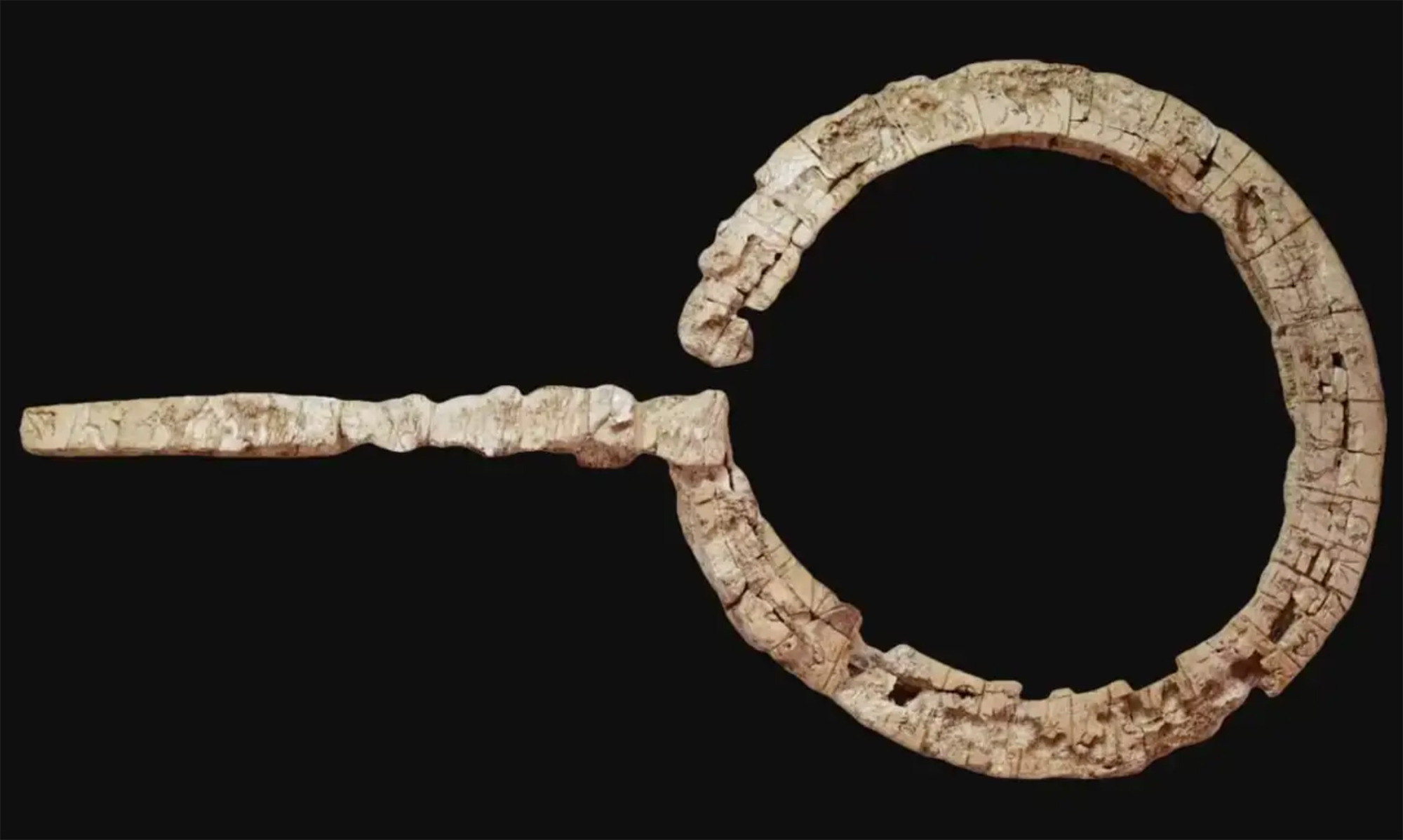
Linear A is a Minoan script used 4,800-4,500 years ago. Recently, in the famous Knossos Palace in Crete, a special ivory object has been discovered, which was probably used as a ceremonial scepter. The object has two inscriptions; one on the handle is shorter and, like most of... [+]
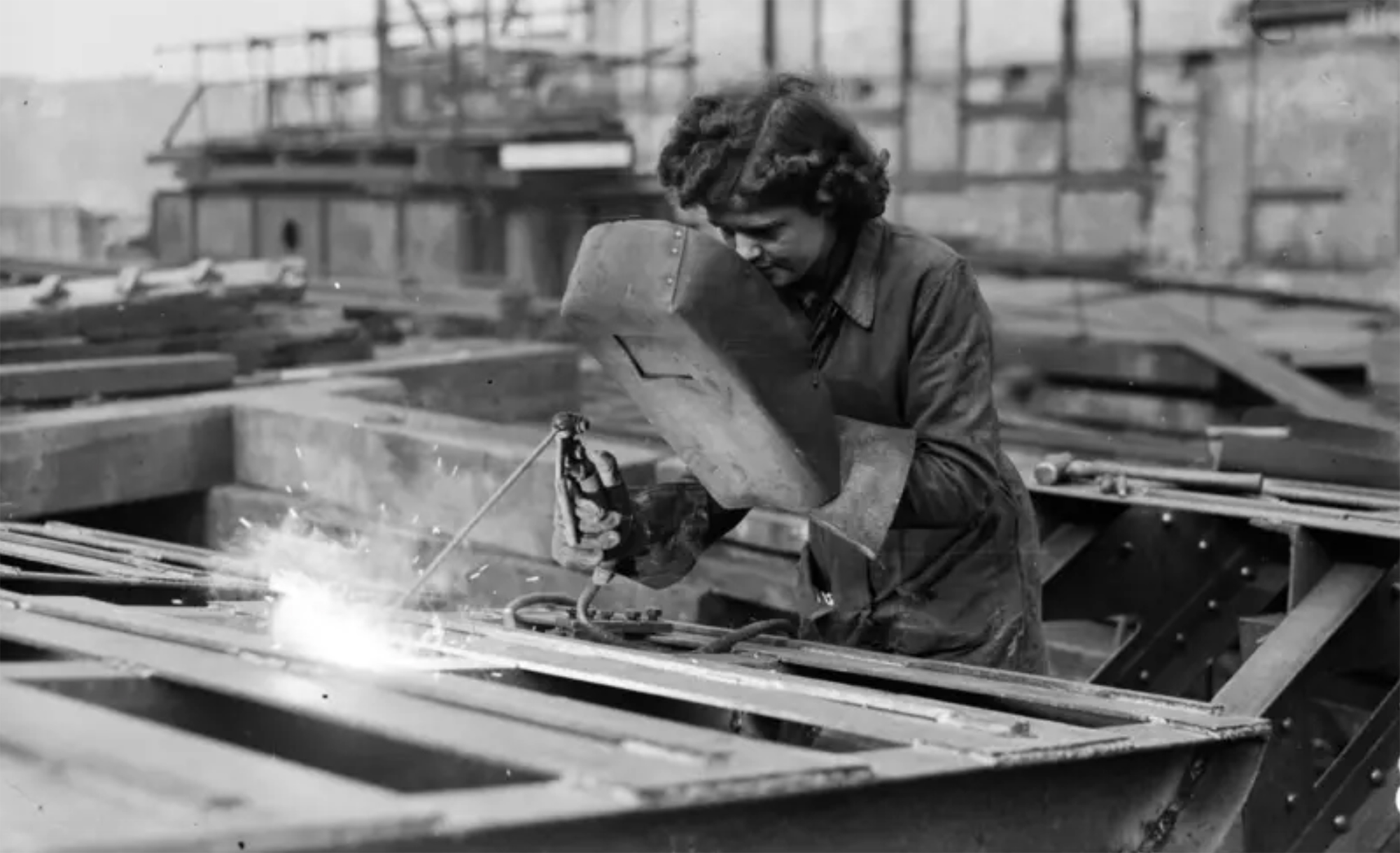
Londres, 1944. Dorothy izeneko emakume bati argazkiak atera zizkioten Waterloo zubian soldatze lanak egiten ari zela. Dorothyri buruz izena beste daturik ez daukagu, baina duela hamar urte arte hori ere ez genekien. Argazki sorta 2015ean topatu zuen Christine Wall... [+]