Of the harvest and of what is necessary to move forward
- What has been done to normalize Euskera in the world of work and what is needed to move forward? To answer these questions, six agents met around the round table on 7 October at the IMH seminar. Each of them took their photo out of the watchtower. Overall rating: sour sweet.
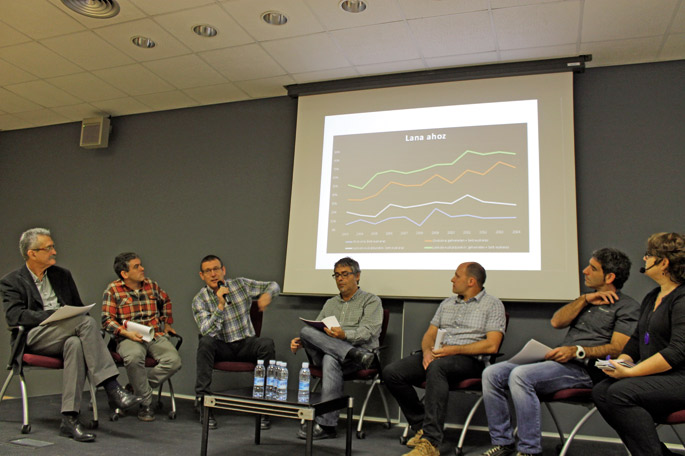
The Elgoibar Machine Tool Institute (IMH) organised the 30+10 seminar for the 10th time on 7 October. Using the round number, they paused to reflect on what the process has so far given. We have brought here a few strokes from the round table which served as a reflection.
More than spreading, keeping what already exists
The director of Research and Coordination of the Vice-Ministry of Linguistic Policy, Jorge Jiménez, collected the steps taken from the beginning of pilot experiences in companies in 1991 to the present day. In the last 18 years, 418 companies have processed their Basque plans through grants from the Basque Government, which have affected 84,000 workers. Gipuzkoa has been the territory where it has contributed most to the normalization of the Basque Country, with 230 companies supported by the Basque Government. The Vizcainae have been 160 and the Alavesas 28. The companies that between 2008 and 2014 obtained the quality certificate in Basque Bikain from one category or another, collected 24,000 workers.
Among other things, Jiménez offered two news items. On the one hand, over the next year, 65 companies will carry out language assessments on more than one occasion. On the other hand, professional associations have been open to aid for the first time and have been well received; for example, the three CAV bar associations have voted in favour. Making the way yes, but Jiménez himself (he was not the only one who had that opinion) said that “the results are, on average, fables.” Aware that the normalization of Euskera has only affected a few CAV companies, Jiménez has taken the view that dissemination is not the priority, but efficiency, that is, to improve the results obtained so far, to perpetuate what has been achieved and to turn these pioneering companies into examples of others.
Need to preserve Euskaldunes spaces
At the request of UEMA, Gaindegia has carried out several studies on the situation and evolution of the socio-economic characteristics of the municipalities of Euskaldunes. The coordinator of Gaindegia, Imanol Esnaola, focused on the Basque territories and highlighted the main characteristics of the socio-economy, which can influence the normalization of the Basque country. In Basque soils the industrial sector has weight, there are companies of a certain size. Conversely, the future is present in highly skilled workers and in the high-tech industry, where municipalities in Euskaldunes (small municipalities in general) are immersed. As the population is scarce, unemployment can have a direct effect and it is very likely that the ten workers of the closed company will be transferred to the surrounding villages, which may be municipalities much more Castilian than the one of origin. For this reason, Esnaola insisted on the need to carefully maintain the socioeconomic environment of the Basque lands, since they contain the greatest Basque potential.
Translate computer tools to Basque
IMH Manufacturing Network Director Tkgune de Innovación, Fermin Lazkano, believes that the process of Euskaldunisation of the world of work will be slowed down. This has not yet been the case, because we have started to work late compared to other areas (leisure, teaching, administration...). He mentioned two factors that will make Euskaldunization slower than accelerated. On the one hand, the lack of enthusiasm, that is, that despite knowing Basque, both orally and in writing, is often done in Spanish. On the other hand, Lazkano has calculated the combinations between the four elements involved in the workplace (employees, tools, colleagues and customer suppliers). The type of relationship most frequently repeated is between the worker and the instrument. For Lazkano, this information is very important, since most computer tools are not in Basque, so the relationship with workers is not only in Spanish, but also in the language of relationship with colleagues and clients. He prioritized the use of Euskera in computer tools, as well as expanding more strongly what is in Euskera, “there are advanced traction companies, but most do not know anything, they do not even know it exists www.euskara.euskadi.eus.”
To show what is to be done, she gave a survey to Vocational Training students: 8 out of 10 students are able to work in Basque; 6 out of 10 would want to work in Basque; 3 out of 10 get to practice in Basque.
Promotion yes, regulation also
In the opinion of Council Secretary General Paul Bilbao, the process of euskaldunization of the world of work has four pillars: companies, workers, clients and public entities. He highlighted the path taken by several companies in the Basque Country and how they will be creators to make the leap into agents. Recently, the Council has promoted the Euskaragileak Works Council, composed of 13 companies, all of them pioneers in Euskaldunisation. They intend to influence other companies and, for example, they intend to start working soon with suppliers. It called for the active participation of trade unions in working in the field of workers, but it is aware that the climate between them today makes it difficult to work together with all of them. The client talked about empowerment, “Why aren’t we going to harness our power to drive the process of Euskaldunization?” The institutions are given two functions: promotion and regulation. Bilbao considers that public institutions have been based on promotion and that the way of regulation is yet to be explored. It considers that the regulation has yielded interesting results, as with the adoption of the consumer decree and the application of recruitment criteria, the number of Euskera plans in companies increased considerably.
“Why not in the Basque workplace?”
DanobatGroup (Elgoibar) chairman of the Basque Committee, Jon Mugartegi, gave a practical example to the round table. In the company, attempts have been made to respond to the demands of some workers that Euskera be the working language. At first, 60-70% of the workers were bilingual. This Machine Tool company sells 90% of its production abroad, but in spite of that, the question of the workers is: “Zergatik ez etxean euskaraz?” The process of Euskaldunization is based on three pillars: linguistic criteria, linguistic profiles in all jobs, and Euskera commission. Nowadays, Euskera is known for about 85% of workers and in assemblies it is used in the same proportion. Another thing is the language of the hallways. According to the 2013 usage measurement, between 40 and 45%. Over 90% of new employees are bilingual.
Gradually in Vocational Training
Before starting the round table, from Laneki, the Association for the Promotion and Improvement of Vocational Training, we heard a comprehensive summary of the situation. The dual training, which works and studies at the same time, has not taken place in the process of Euskaldunization; in the permanent training there is a red light, as no progress is made; and training in work centers is the field where the strongest steps have been taken.
Lanekin's President, Rikardo Lamadrid, has stated that Basque Vocational Training is an example in the world, that it is no coincidence that it is, and that this affects, for the better, the health of the Basque country. However, he acknowledged that we are improving, but that we are humble.
Gasteizko 1 zenbakiko Auzitegi Kontentzioso-Administratiboak emandako epaia berretsi du EAEko Justizia Auzitegi Nagusiak. Lan poltsan parte hartzeko euskara maila altuenaren baliokide diren 3. eta 4. eskakizunak indargabetu zituen Gasteizko Auzitegiak.
In recent months I have had to work in a number of institutes and, at some point, I have had to talk to the students about the possibilities offered by the labour market. The typology of the students is varied and in the same city varies a lot from one neighborhood to another,... [+]
Languages Lan has just organised the first international conference on linguistic management in Bilbao. Much has been said in the Congress about language policy, management and tools. And emotions. And from emotions, how many cooperatives, companies and organizations in our... [+]
Few spend their whole lives at the same work. What was common at the time of our parents, today, is absolutely unusual. It seems that millennial generation youth will not spend five years in the same job and the time will be much shorter between Z and Alpha generations.
I too,... [+]









.jpg)







