Foods without cereals or milk
- Paleodiet, hypotoxic regimen, old diet... Some have come to this way of life by pure empiricism in the fight against a disease, others by criticism of modern food and well-known and poorly proven regimes. They're multicolored heterodoxas.

"Are you in the macrobiotic? they'll ask you all here as soon as you hear that you're dealing with a serious or chronic disease. Young people looking for alternative ways of life choose to feed on vegetarians and even vegans. The cytes appear at the top of the food pyramid that the family doctor has in his office. Curious, how stablishment and heretics come together in the worship of cereals and legumes.
But there are also many who in the world, in addition to milk, consume meat fish without difficulty and avoid them precisely. Oh, milk, to make our children older, and for those of us who are of age, especially women, who are supposed to be indispensable! No, then, the voices of those who give up on them are becoming more and more frequent.
Improve with the transfer of sacred specimens
The author of this chronicle recognizes that he is not a neutral storyteller: like many others suffering from arthritis or other serious or chronic diseases, he has also come to live without cereals, not only by a doctor or a healer, but on the recommendation of other patients with the same problem. By pure empiricism I came to the starless, even narrower than we will call Paleodiet, to speak with simplicity, as I explained in Article 2106 of Argia, the doctor who at one time found therapy too cheap for spondylitis.
Among patients with a special arthritis that is spondylitis is known the English forum www.kickas.org, in which there are hundreds of testimonies that have managed to improve their lives by changing their diet. Like Kickas in English, you can read in Basque www.izorrategi.org or Spanish www.elblogdelalmidon.org and more.
Those who have spondylitis reject cereals with starch, potatoes, legumes and other manipulated foods, based on the theory built by British doctor Alan Ebringer to understand the espondilitis.El case that these patients, after several months of transition, although they tear apart the orthodox pyramid of food, besides improving in inflammations, show balanced blood tests.
The British Carol Sinclair in his book Low Starch Diet told us how he came to a similar feeding system by his own means. Suffering from pain in the irritating colon since childhood, after testing several therapies and following the indications of his intestine, he came to reject cereals, particularly all starches.
Without insisting so much on starch, there are more diseases that have generally been improved by the form of food that can be called paleolithic. Specifically, L’Alimentation ou la troisième médecine (in Spanish, edited by Integral), which claims the election of Dr. Jean Seignalet.
In the book “Les abeilles soignen ma Sclérose en Plaques” (The bees take care of me the Multiple Sclerosis) this woman from the surroundings of Marseille naively recognizes the improvements due to the alteration of the diet, recognizing without hiding the limits of the improvement.
Jean Seignaleten ancestral regime
This doctor from Montpellier could serve as an example to the old doctors. I pioneered renal vaccination, immunology expert, researcher, professor, at the same time that I cared for patients of many classes in the clinic... in the conversations I recognized that the privileged man felt in times when knowledge has been specialized and far from the practice.
In Spanish, Food or the Third Medicine is the book that has been designated as a witness of the wisdom of Seignalet. He describes through 560 pages the details of each of the evils to which the regime has applied, including its successes or failures with the sick, explaining at the beginning of his book his choice and its causes, recognizing that he has drunk from Kousmine, Burger, Frandin and other sources of wise men who have occupied human food.
Seignalet in the Neolithic is the key to the major diseases. “Since our species separated from the anthropoid apes, five million years ago, human ancestors (homo habilis, homo erectus) and the same homo sapiens have been fed the same types of food. Our ancestors were nomads, collectors/hunters, which means they ate meat, fish, eggs, honey, wild cereals, vegetables and fruits. When children, they drank only their mother's milk. The fire was invented about 400,000 years ago. However, there is no evidence that more than 10,000 years ago the fires for cooking the food to which it was intended have been initiated. (...) We can say that cooking was little or nothing complete.”
Therefore, although with industrialization and above all with consumerism the damage of the thousands of products that have been introduced into food has been evident, the problem comes much earlier for Seignalet. In some places, 9,000 years ago and in ours, much later, there were the main changes in human nutrition: they began to eat domesticated (non-raw) cereals that have been very different from the wild of origin, to drink animal milk and to eat many cooked foods, to the detriment of the human being.
The organism developed over the last billions and millions of years is introduced to many elements of the intestine that it does not know. Later, industrialization will lead to new and more serious problems: industry and entry into kitchens produce new processed oils, food is contaminated with both pesticides and medicines applied to animals, added to last longer and all kinds of poisons. To this must be added the fact that the qualities of synthetic fertiliser doped crops have rapidly deteriorated.
When these unknown issues have got into the bowels of the man that the organism has organized over the past billions and billions of years, it causes three kinds of problems. Some begin to destroy the immune system, mixing in the fight against new molecules. Immunity leaves others the way, but they are obstructed in one part or another of the body. Human beings who have a third category of diseases can assimilate these molecules, even allowing them to circulate without obstructing, but not manage to expel their waste.
Click the Internet to view “Pale Diet”
Seignalet’s choice is therefore to return to pre-Neolithic foods: outside cereals, except rice and buckwheat; out of dairy and dairy products; eat as much as possible of raw fruits, vegetables and nuts; that oil be vegetable; that virgin olive oil be cold-pressed; prioritize biological products; do not smoke or fry, cook. From there the details and recommendations of what he calls ancestral regime and hypotoxic diet are expanded.
It cannot be said that the proposal to feed itself in a similar way to pre-Neolithic collector hunters is unique, you just need to look for it on the Internet to realize it. There are many proposals, including differences, and a lot of products that are sold under the concept of Paleo.
To highlight one in a thousand, one of the classics and translated into Spanish is Loren Cordain. In the preamble to the book The Paleolithic Diet published in 2002, it says: “The problem is that we are genetically adapted to eat as hunter-gatherers ate. Many of today's health problems are a direct consequence of what we eat and don't eat. (...) I haven't invented this diet, nature invented it."
It is also the book Paleodieta for athletes (2007). It is worth mentioning, because it responds to a sports myth: cereals are the basis of good performance. Those who follow the proposals of Seignalet or alan Ebringer (a diet without starch) to treat a disease will find in that book some guidelines for continuing to practice sport.
Moreover, from the literature that you will find on the paleotic diet, many have called as: “Lose weight and gain health from the diet that nature designed for you.” That Kellogs does not have exclusive marketing.
Anthropological bases
Among those who have explored the feeding of pre-Neolithic human beings in the references they give us to the twenty-first century, it is worth mentioning Staffan Lindebg. Doctor and professor at the Swedish University of Lund, Lindebig has tried to critically analyse the scientific bases of food models known today in the rich world. Anyone who promotes any form of food demonstrates some scientific study as a guarantee of their proposal.
Lindebig has reached the following conclusions, as it can be read on its website: “Food recommendations for people’s health are built on such an uncertain basis that the medicine of evolution [human] can greatly complement the results of traditional scientific methods.(...) Nutritional recommendations should be developed for the prevention and care of Western diseases, taking into account as far as possible the biological heritage of the human being. Foods that have been on the human diet for less than 10,000 years should be analyzed with a critical eye before recommending people as a staple food.”
Lindebig and his team have been studying the health and ways of feeding people who until recently have lived hunter-gatherers on the island of Kitava in Papua New Guinea, because many of the keys to the future life of human beings are in the footprints of what our ancestors did.
He who is in good health may ask: “What is all this for me if I don’t have cancer, arthritis, multiple sclerosis, hypertension?” On the other hand, who, in the whirlwind of a diet, fears falling into a kind of sectarian behavior, will ask: “Where do I find something I’m sure will help?”
The wise advice of Michael Pollan
The journalist Michael Pollan has come up with criteria similar to those described in these lines, forcing him to investigate the history of food and food. The detective in the supermarket, decorated by his Defense of Food Itsusi, offers interesting handles. It has not put into vain the second title: “Eat well for science and advertising to deceive you without leaving it.”
Misleading the sciences? Yes, if it forces you to devour as truth what you know at a given moment. It is no coincidence, says Pollan, that Justus von Liebig is both the forerunner of industrial agriculture and industrial food. By the end of the 19th century, both were planned with knowledge of science, as well as synthetic fertilizers and papilla with cereals instead of breast milk for children. Then it was seen that they both had great deficiencies. Since then science has been filling the holes of knowledge with new information (vitamins, trace elements...) but it has a lot of misunderstanding. And what is more than a living diet?
Pollan marks two major leaps in human ways of feeding. One, the one from the Paleolithic to the Neolithic cited. The second is the time of industrialization that we've been in for the last 150 years. The first was that of the above mentioned changes, cereals, dairy, cooked and reduced biodiversity of food, eliminating hundreds of species of plants that until then were collected and eaten.
In the subsequent centuries, human groups have been adapting to the new food, each with its peculiarities. The same would explain why, for example, in some groups the ability to sanction milk is more common than in others. The industrialization of 150 years ago has brought with it even greater changes that Pollane describes in detail.
Today's modern breads have been imposed on whole foods, on breads made with all the ground flour in their muela. The diversity of species and food has decreased considerably: compared to the hundreds of previous plants, we now only eat a dozen, mainly wheat, maize, rice and soy. We eat quantity more than quality. We've gone from eating leaves to eating seeds mostly.
The Pollan proposal is to put the whole development of the situation above all. You don't eat anything your grandmother's grandmother doesn't know as food. Avoid those containing unknown or curious elements. Run away from the supermarket. Discard those who advertise good properties... as they come packaged.
Without condemning dairy products or cereals to hell, they mainly eat plants. In plants, leaves are more abundant than seeds. Eat as varied as possible. Eat food grown on healthy land. When you can eat strawberries from plants, fruits and fish. Distrust new foods that are not the usual ones.
At the head of everything, Pollan has a claim that coincides with Slow Food: it regains the pleasure of eating. “Let us reclaim the health and happiness of the diner.” Not eating alone with sadness, but eating together with pleasure.
Jauzarrea fundazioak deiturik (Xabi Otero argazkilaria dauka presidente) bigarren urtez burutuko da Irungo Ficoba erakustazokan Atlantiar biltzarrea. Maiatzaren 17ko ekitaldiak izenburutzat darama “Ehiztari-biltzaileen garaitik gizarte ekoizleen garaira”. Egitarauan iragarritakoaren arabera hitzaldietan orriotako kontuetaz larregi arituko ez diren arren, justu aipatu dieta proposamenok gakotzat daukaten aroaz jardungo dute.
Gaztetxo ginela eskoletan irakatsi zitzaigun historian Neolitikoa ikusten zela gizakiaren aurrerapauso garrantzitsutzat. Gaur askok ikusten dute trantsizio hori gizakiaren gehiegizko populazioak eragindako aldaketa moduan, aitortuz ekarri zituen aurrepenekin batera eragin zituela kalte handiak ere gizakien bizimoduetan: bioaniztasunaren galera, gaixotasun berriak elikaduraren murrizteagatik eta populazioen pilatzeagatik, bizimoduaren gogortzea, zanpaketa sozialen gogortzea, gerren ugaltzea...
Badira adituak zenbait gaitzek daukaten osagai genetikoa lotzen dutenak gizaki batzuek oraindik elikagai berrietara egokitu ezin izanarekin. Bestela esanda, eboluzioak –epe luzeetan jokatzen duelako– oraindik arras bazterrean laga ez gaituen talde genetikoetako ale errefusak ginateke. Edo egoskorrak, nondik begiratzen den.
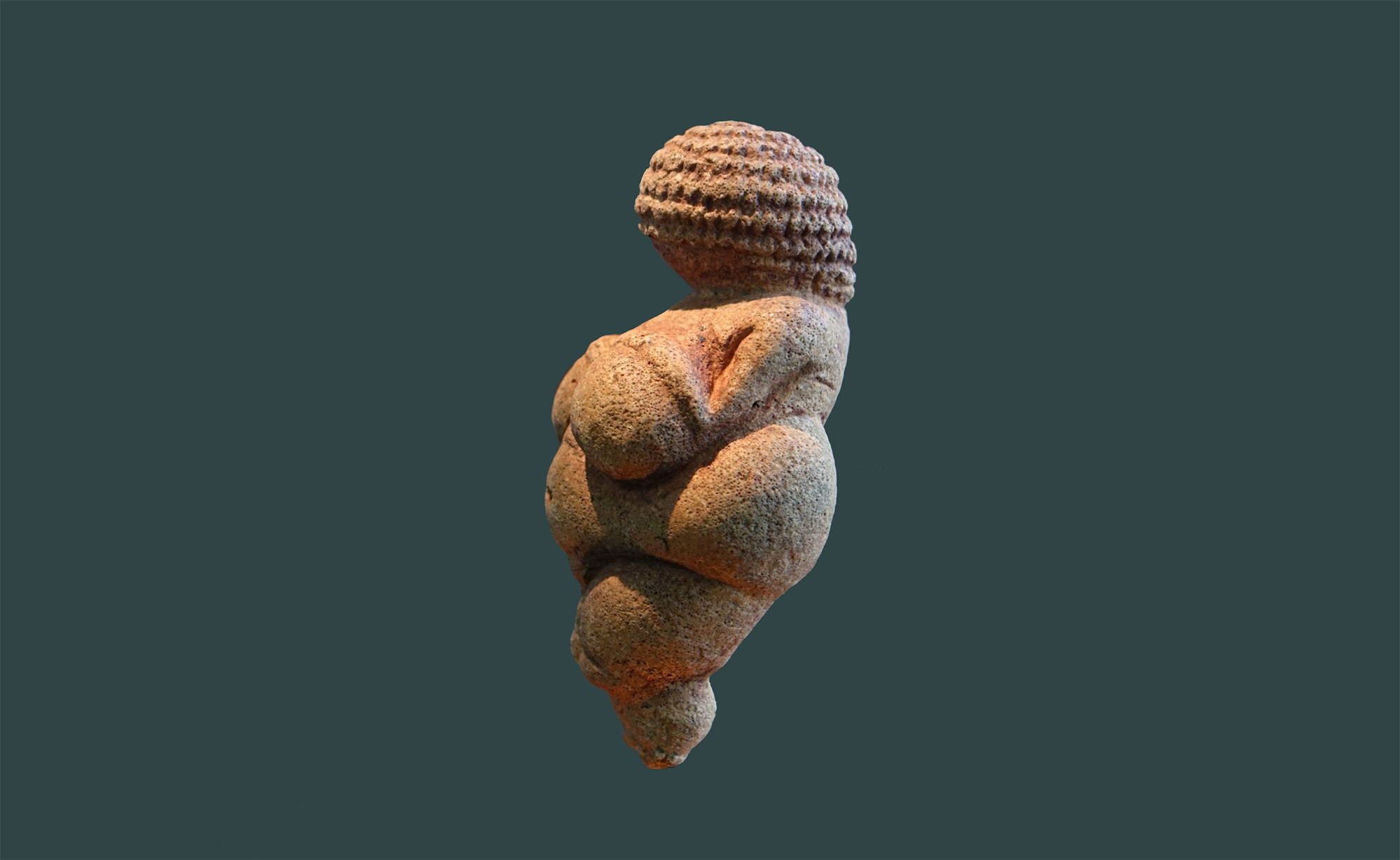
Willendorf (Austria), 1908. At a site in the Wachau Valley, archaeologist Josef Szombathy found a small anthropomorphic statue of a woman about 11 cm, carved in stone and dyed with red ochre.
Since then, it is the best-known venusi of the Paleolithic and has been analyzed from... [+]
1891n nekazari batek Gwion estiloko hainbat labar pintura aurkitu zituen Kimberlyn (Australia).
Font Major kobazuloa (Tarragona, Katalunia) 1853an aurkitu zuten eta urte asko dira bertan arkeologoak lanean ari direla.
Bizkaiko Aldundiaren esanetan duela 14.000 urteko grabatu multzoak "kalitate tekniko argia" du eta berezia da irudiak "oso argi" ikusten direlako.
Zientzia elkartearen ustez haitzuloan historiaurreko aztarna gehiago aurkitzeko “aukera handiak” daude eta eremu osoa babestu behar da.
Orain artean ezezagunak ziren eta Nafarroan aurkitutako zaharrenak lirateke. Hori dela eta, Aranzadik leize ondoko harrobiko jarduerarekin ez jarraitzea gomendatu du.
SOS Alkerdi, Urdazubiko ondarea babesteko plataformak Berroberria, Alkerdi eta Zelaieta inguruko leize babestuetan gertatzen ari dena ezagutarazi du. Gune horretan dago gaur arte ezagutzen den Nafarroako labar arte paleolitikoaren kokaera bakarra. Haien gainean harrobi bat dago;... [+]
Asteartean aurkeztu zuen Bizkaiko Aldundiak paleolitiko 70 pintura eta grabaturen aurkikuntza. Berriatuako Udalak ez du inolako informazio edo berririk izan orain arte.
1992an Shiyan Beicun herritik hurbil, Txinako Zheijang probintzian, herritar batek Longyouko haitzuloak aurkitu zituen. Urez beterik zeuden eta horregatik naturak sorturiko leize nahiz haitzuloak zirela uste izan zen hasieran, baina urez hustu ondoren gizakiak eraikitakoak... [+]