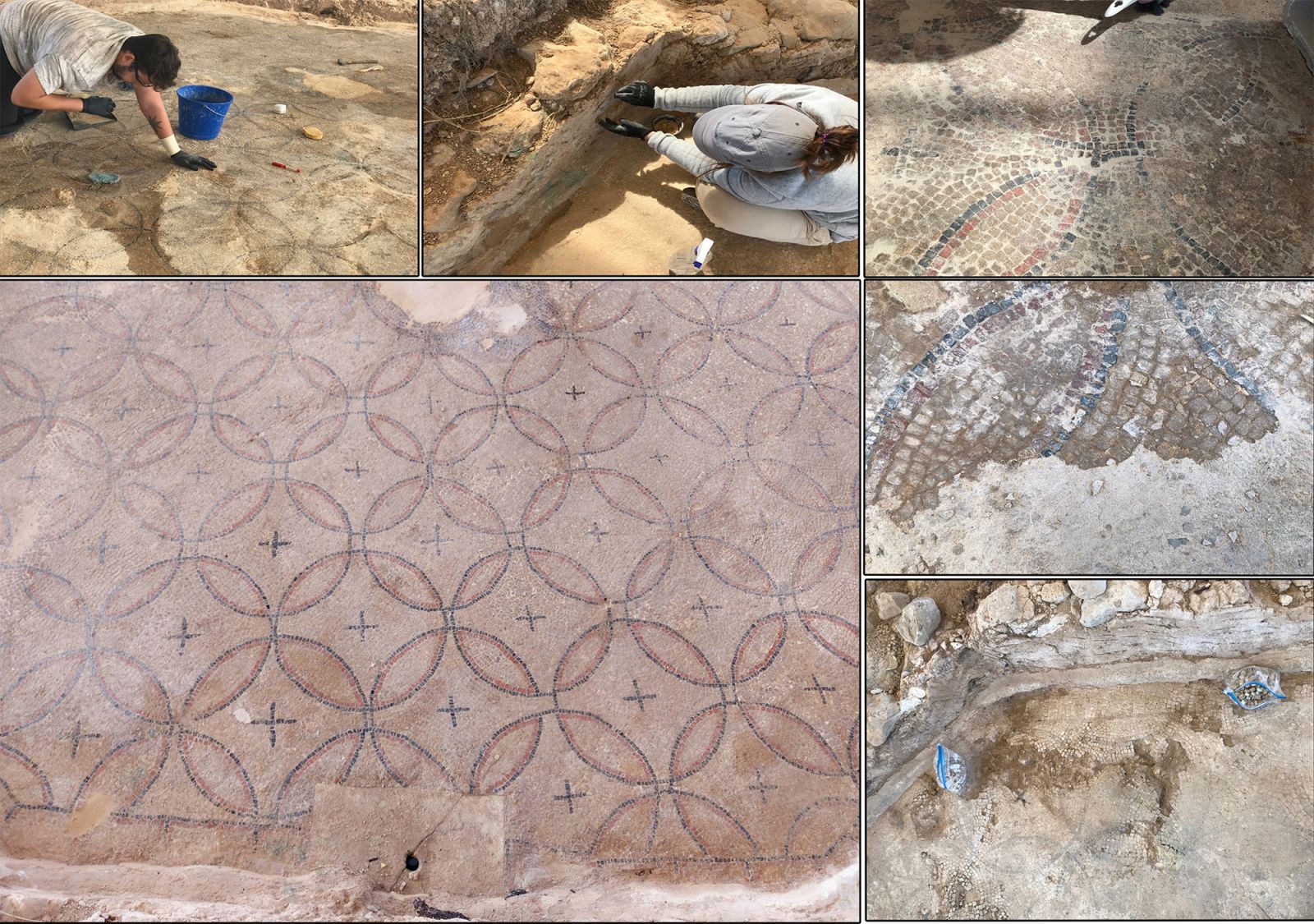
Exhibition in Ablitas of one of the most important Roman mosaics found in the Basque Country
- The great Roman mosaic discovered in 2017 at the site of El Villar has been restored and exhibited in the house of culture of Ablitas. The 4th century villa or farm occupies an area of 40,000 square meters and is believed to be in its entirety, although only a small section has been excavated. Among the heritage found are a bronze sculpture of the god Cupid, rooms with hypocraters and the mosaic itself.

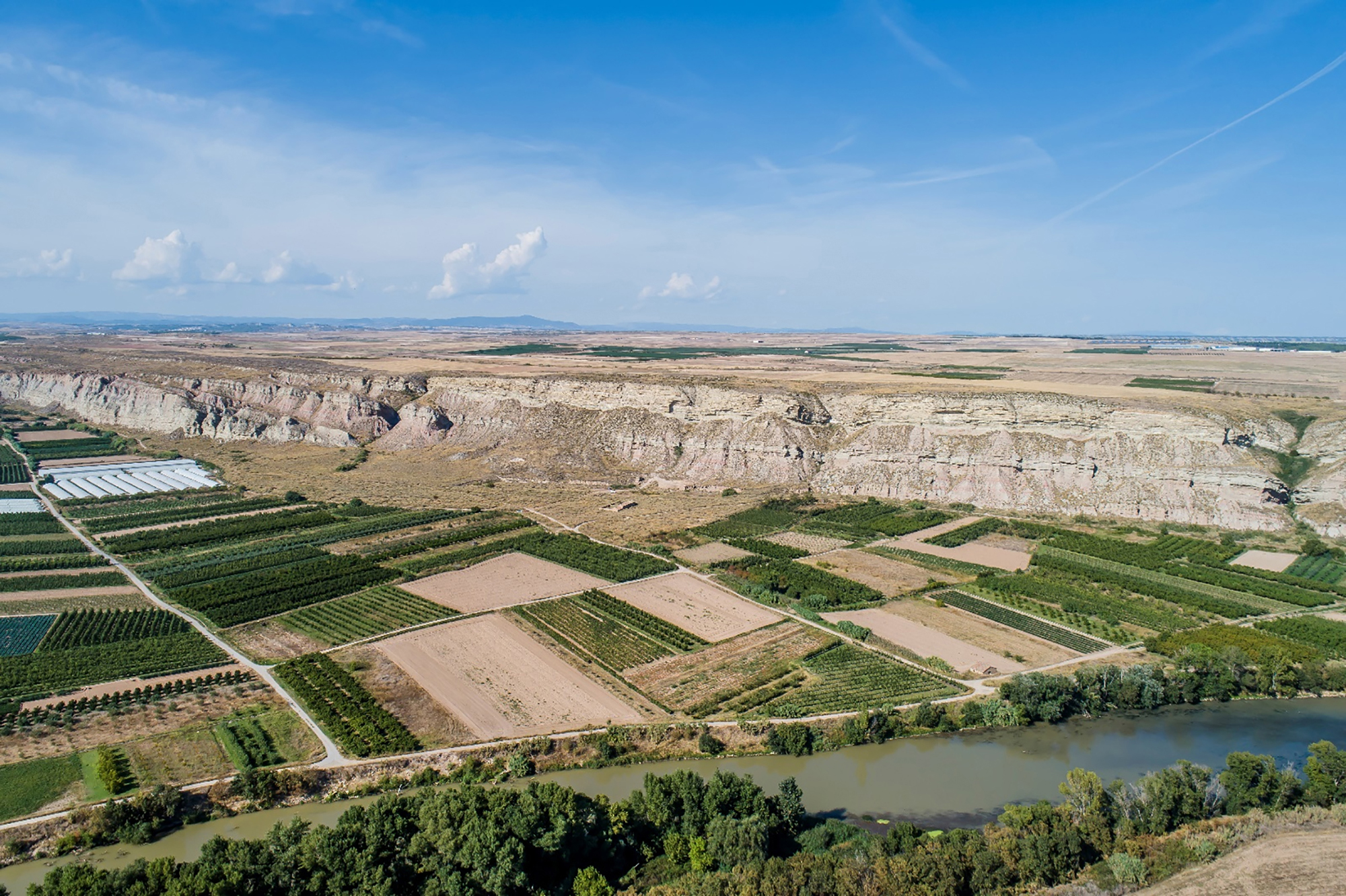
In Ablitas, in the Ribera de Navarra, there can still be many archaeological treasures of the Roman era, which can give the opportunity to know how the people of 2,000 years ago lived. Gradually the deposit of El Villar is being excavated, not far from the urban center, and among them is a large mosaic, one of the most important found in Euskal Herria.
The mosaic is three colors (white, black and red) and measures 2.35 square meters. It is estimated that it has 235,000 teselas decorated with 116 rosettes and 108 crossings
At the initiative of the Government of Navarra and the City of Ablitas, the mosaic has been restored and exposed in the house of culture, together with an exhibition that explains the context. The mosaic is three colors (white, black and red) and measures 2.35 square meters. It is estimated that in total it has 235,000 teselas decorated with 116 rosettes and 108 crossings. It is probably similar to other important Roman deposits preserved at the Museum of Navarra.
The mosaic was discovered in 2017 in El Villar in one of the participatory excavation campaigns carried out annually with the neighbors of the area, and since then it suffered damage due to the trajectory of the rodents that were taking off the teselas, and also to not suffer expoliations or robberies, so they have decided to rehabilitate and relocate it.

El Villar, a large farm
The Roman ruins of Ablitas have been known since at least 1925 – as the archaeologist Maria Jesús Berraondo says. At the beginning of the century, there was also a treasure trove of Iberoromanas coins, but outside the stratigraphic and very dispersed context.
The first excavations of El Villar were not carried out until 2010. The site has the trace of a classic Roman farm, and archaeologists say that the entire area can have at least 40,000 square meters, of which some 4,000 are protected and guarded with a fence.
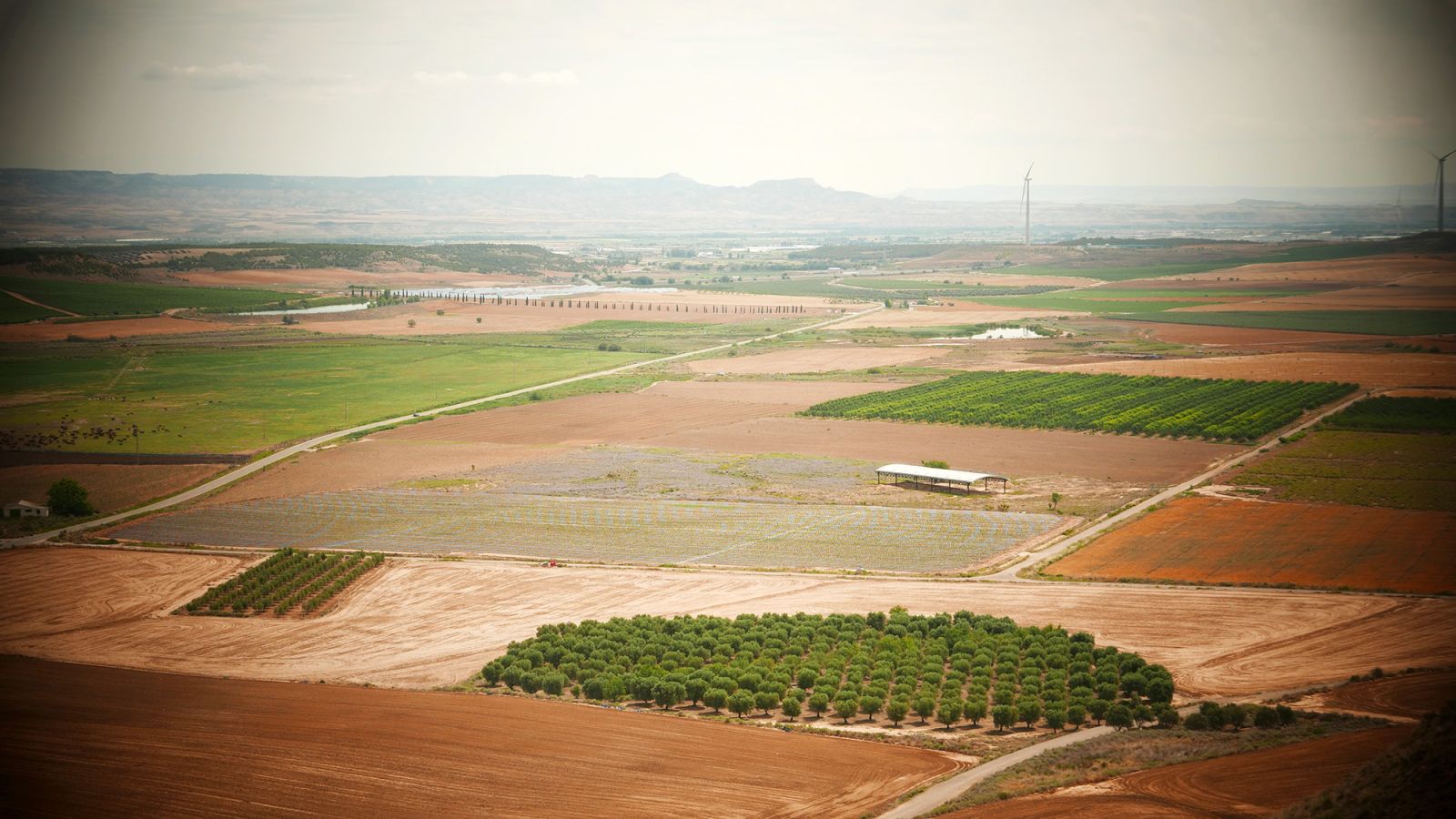

These Roman villas or villae (in plural in Latin -ae) led to the Ribera de Navarra a type of innovative rural settlement, fully dedicated to agriculture. In addition to the areas intended for slaves, animals and crops, the farms also had an urban space – lived by the owner of the house or the Dominus – which is the one that is protected in the Ablitas site, which has seen by Georadar that there are still many buildings in the subsoil.
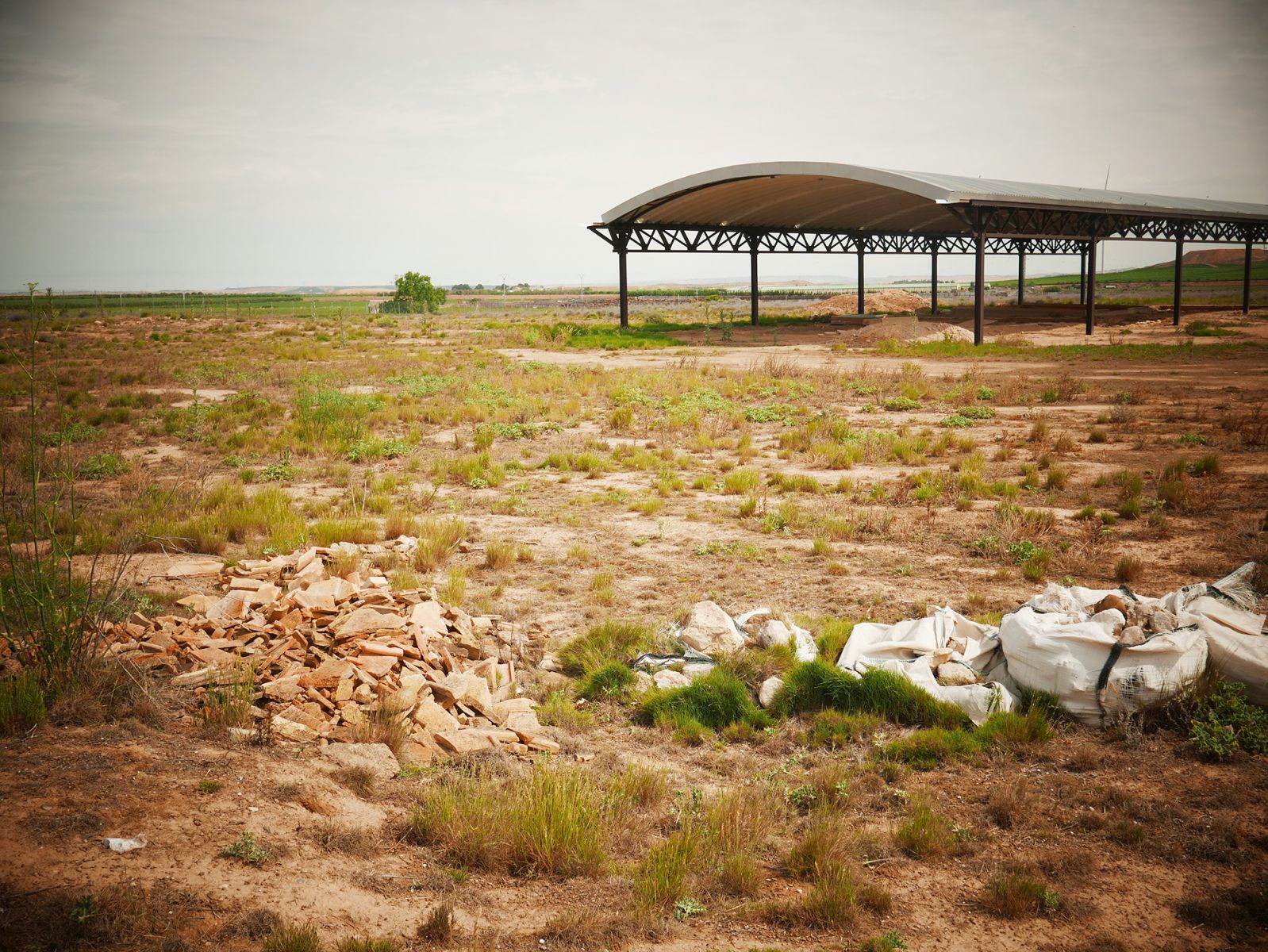

Hipocalero: a house with heating
Excavations carried out so far have detected some of these buildings, including those that have a heating system or a pitcher to keep the soil warm. Ablitaskoa is one of the best preserved deposits in the Basque Country.
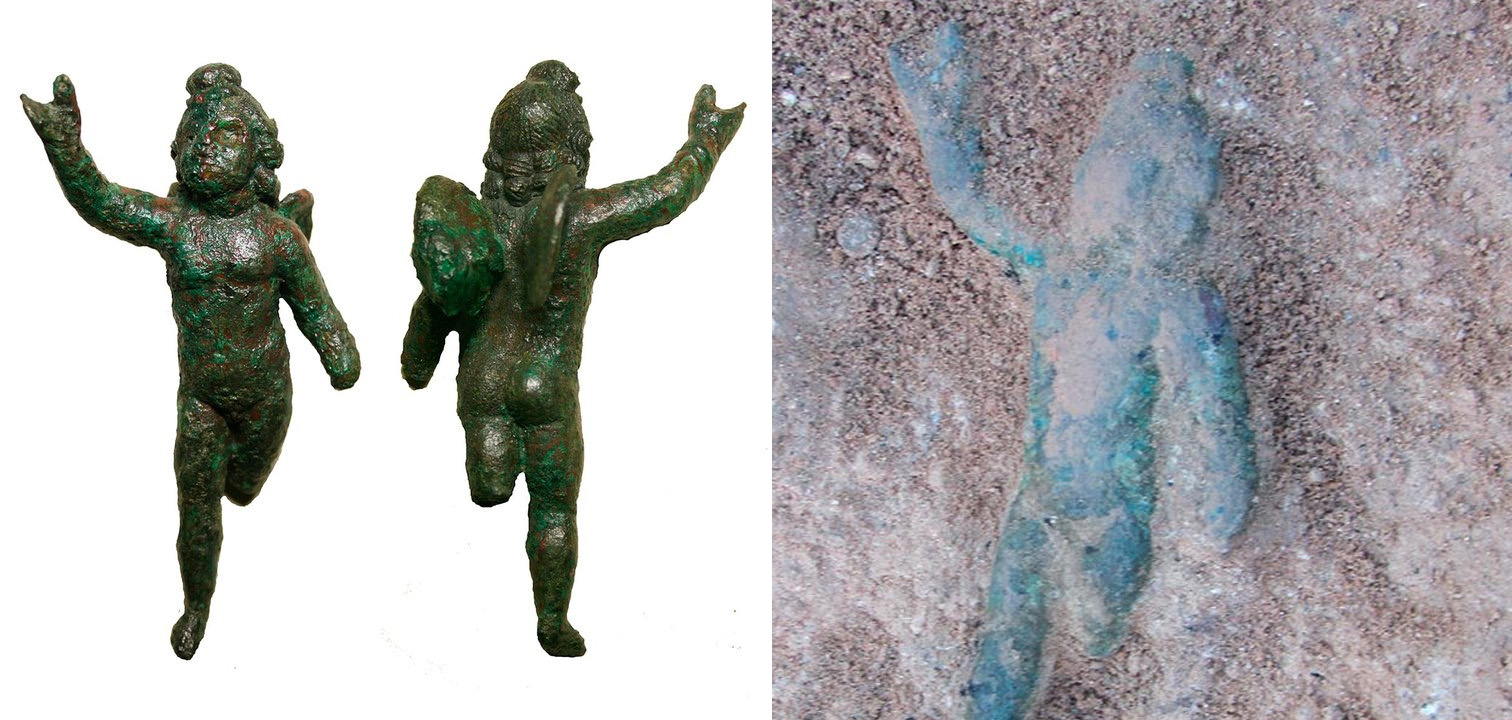
In 2013, a special object was also found in a peristile or passage: A little bronze figure of the god Cupid, very well laid and preserved. It could have a religious function or just be used as an ornament.

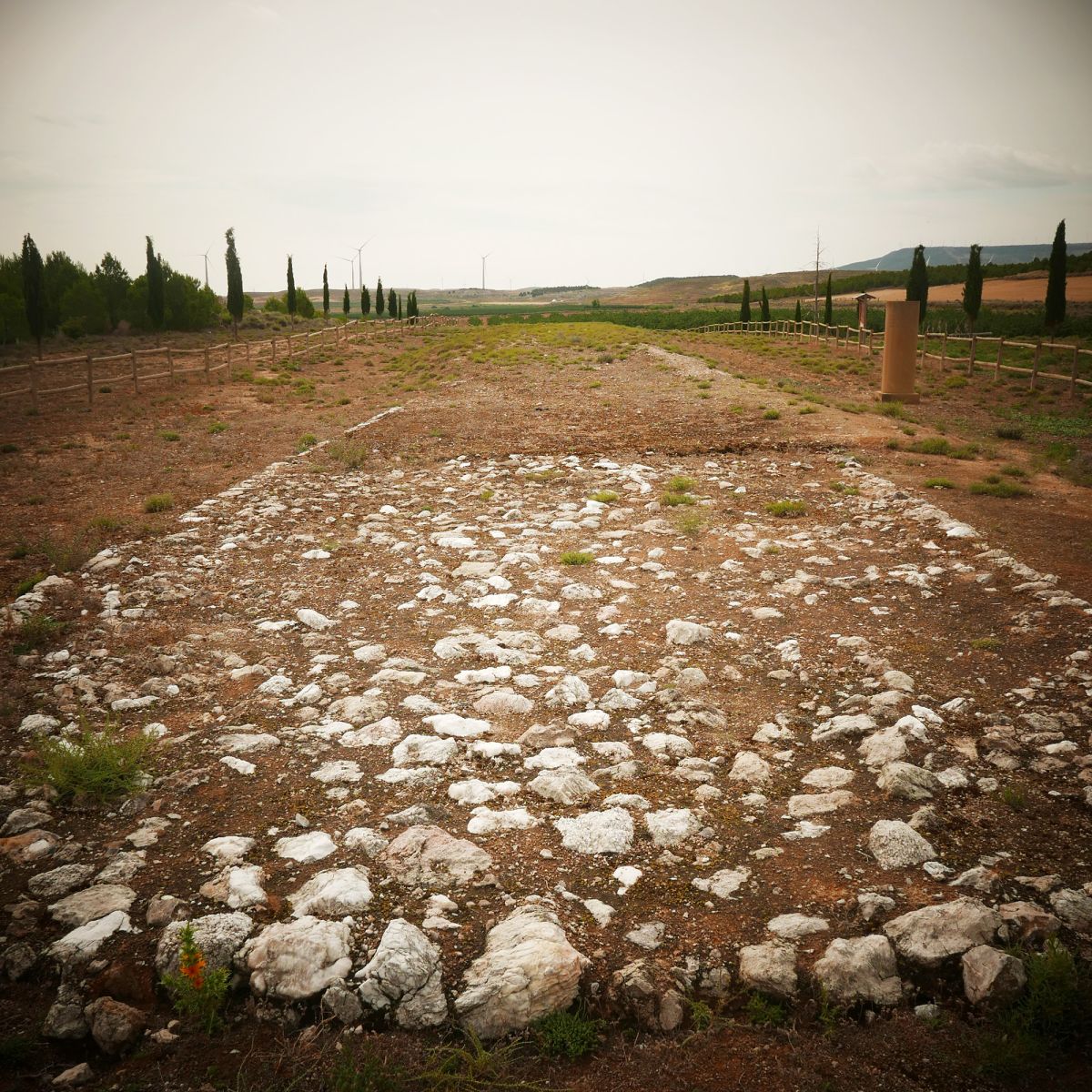
Roman road not far away
The Villar was in a strategic location, close to the cities of Cascantum and Belsinone, along the route that joined Tarraco with Asturica-Astorga. It is not difficult to imagine, therefore, that the crops produced in the area would easily be moved to those cities thanks to the Roman road.
The Romans used complex engineering to build these 40-meter-wide and 100-kilometer "highways": they cleaned the surroundings, raided and laid numerous layers of sandstone and plaster.
In fact, the best parts of this road have been preserved in the area. Just half a kilometer from the site of El Villar they have unearthed the lower part of the road thanks to the fossilization of the names “Camino de los Romans” or “Camino Mallen” (city of Belsione), among others.



In Ablitas, we can see what the roads of communication, the houses, the rural nuclei and the art of two thousand years ago were like. All in a unique decor.
Aranzadi Zientzia Elkarteko Etnografia Sailaren zuzendari berria da Maite Errarte Zurutuza (Beasain, 1995), urrian Fermin Leizaolaren lekukoa hartu ondoren. Kultura materiala aztertzen jarraitzeko beharra azpimarratu du, gizartearen memoria eta bizimodu aldaketak erregistratzeko... [+]
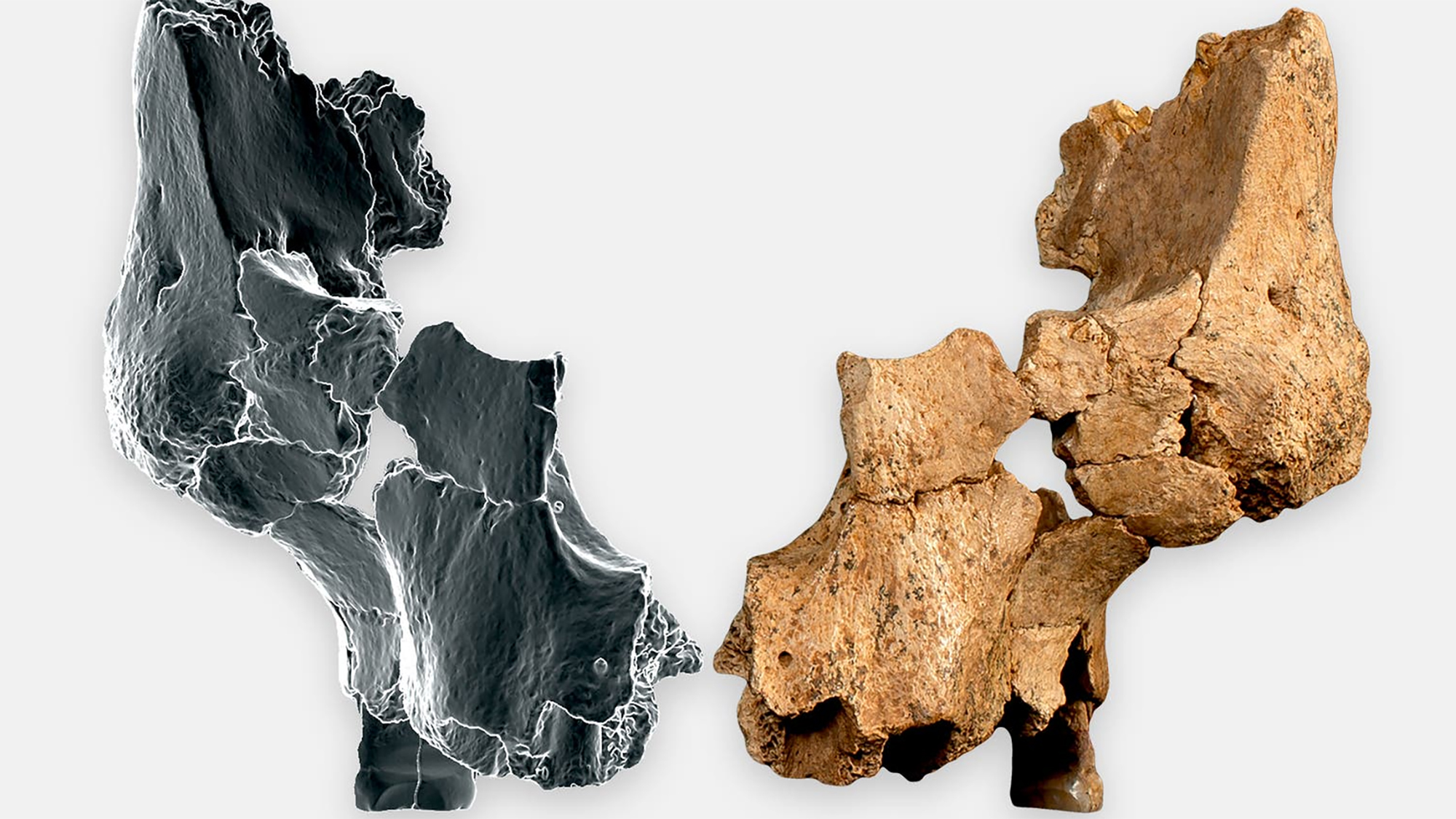
Atapuercako aztarnategian hominido zahar baten aurpegi-hezur zatiak aurkitu dituzte. Homo affinis erectus bezala sailkatu dute giza-espezieen artean, eta gure arbasoek Afrikatik kanpora egindako lehen migrazioei buruzko teoriak irauli ditzake, adituen arabera.
Martxoaren 30erako Iruña-Veleia martxan, SOS Iruña-Veleia eta Euskeraren jatorria elkarteek manifestaziora deitu dute, Aski da! Argitu, ez suntsitu lelopean. Azken bi urteetan "hondeatzaileak sistematikoki eremu arkeologiko oso aberatsak suntsitzeko modu... [+]
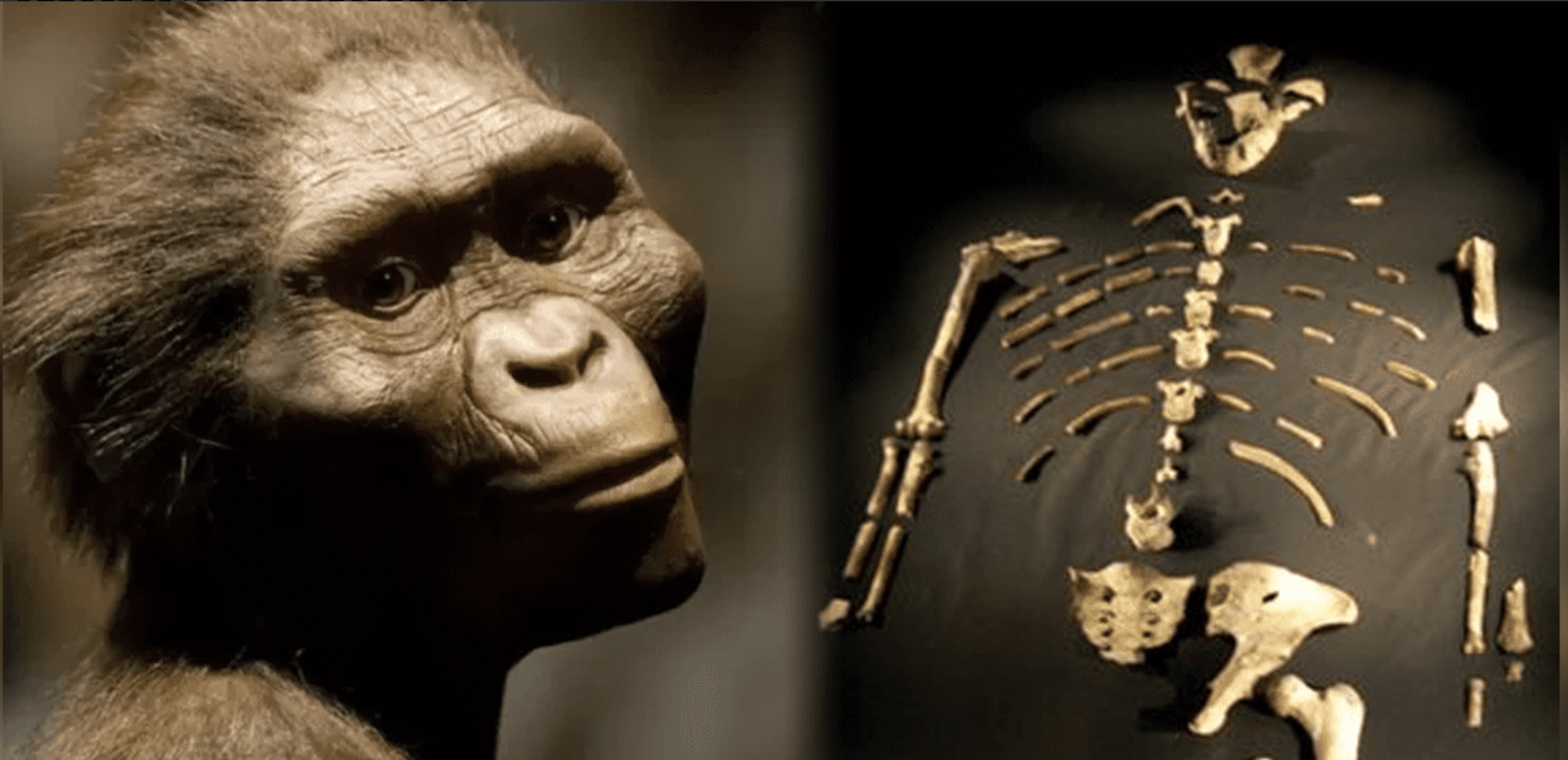
Ethiopia, 24 November 1974. Lucy's skeleton was found in Hadar, one of the oldest traces of human ancestors. The Australian hominid of Australopithecus afarensis is between 3.2 and 3.5 million years old.
So they considered it the ancestor of species, the mother of all of us. In... [+]
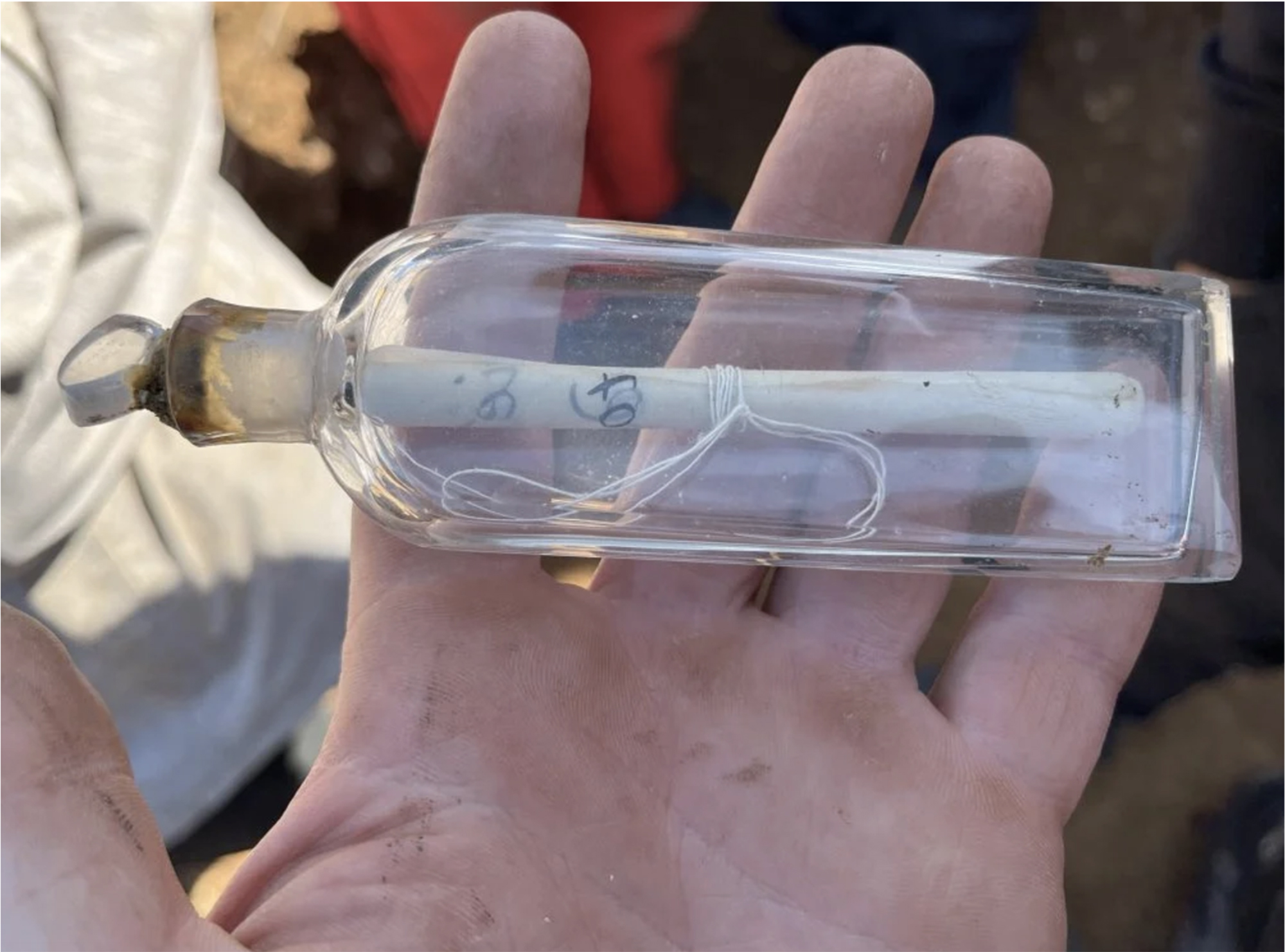
While working at a site in the Roman era of Normandy, several archaeology students have recently made a curious discovery: inside a clay pot they found a small glass jar, of which women used to bring perfume in the 19th century.
And inside the jar was a little papelite with a... [+]
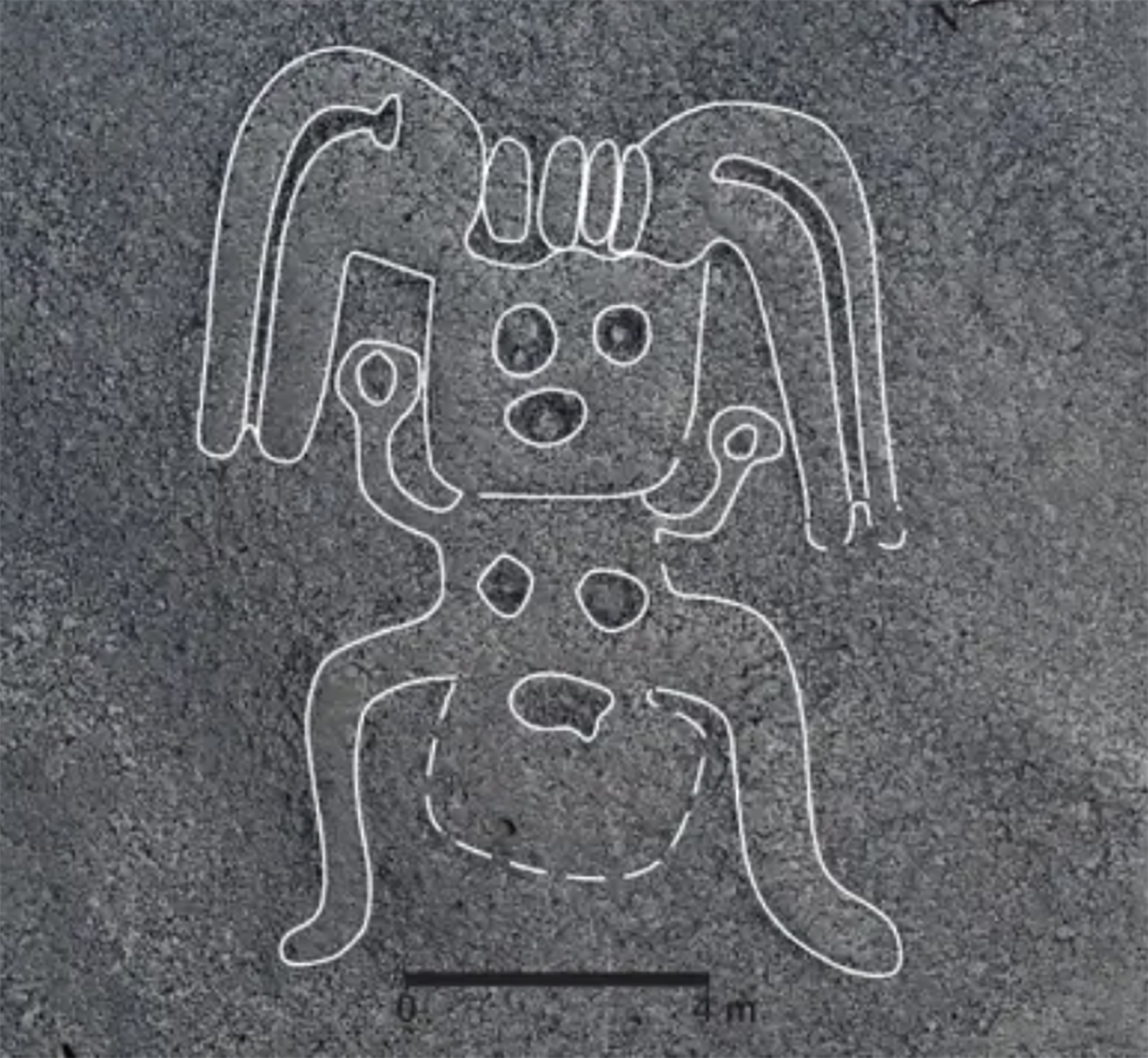
A team of researchers led by the Japanese archaeologist Masato Sakai of the University of Yamagata has discovered numerous geoglyphs in the Nazca Desert (Peru). In total, 303 geoglyphs have been found, almost twice as many geoglyphs as previously known. To do so, researchers... [+]
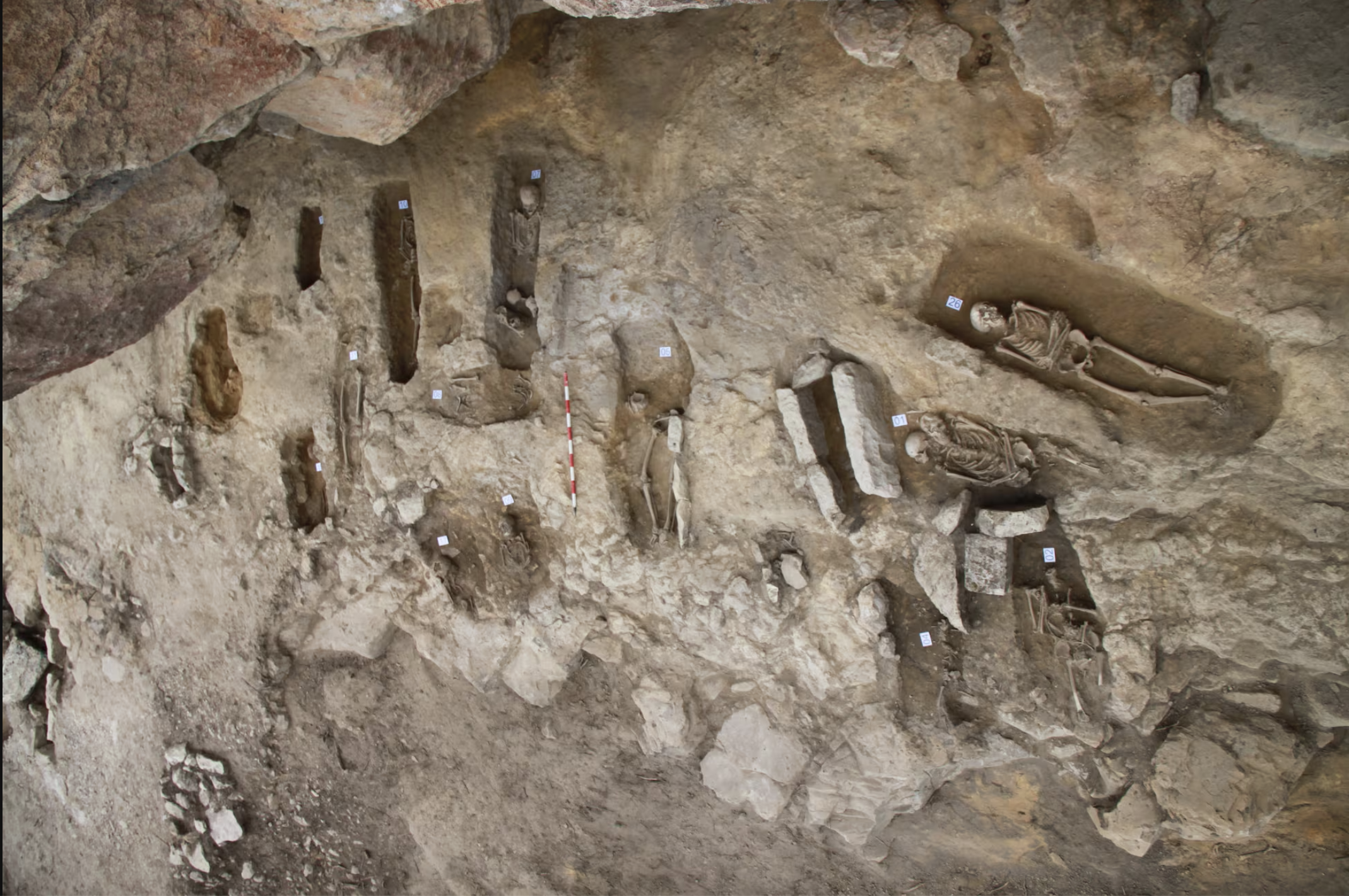
Treviño, 6th century. A group of hermits began living in the caves of Las Gobas and excavated new caves in the gorge of the Laño River, occupied since prehistory. In the next century, the community began to use one of the caves as a necropolis. In the 9th century they left the... [+]
On August 1, a dozen people from the family were in Aranguren. Two young people from Aranzadi made firsthand the excavations and works being carried out in Irulegi. This visit is highly recommended, as it reflects the dimension of the work they are doing.
Halfway, at the first... [+]
In the desert of Coahuila (Mexico), in the dunes of Bilbao, remains of a human skeleton have been found. After being studied by archaeologists, they conclude that they are between 95 and 1250 years old and that they are related to the culture of Candelaria.
The finding has been... [+]
The Roman city of Santakriz is an impressive archaeological site located in Eslava, near Sangüesa. Apparently, there was a fortified people of the Iron Age, and then the Romans settled in the same place. Juan Castrillo, himself a priest of Eslava, gave the site for the first... [+]
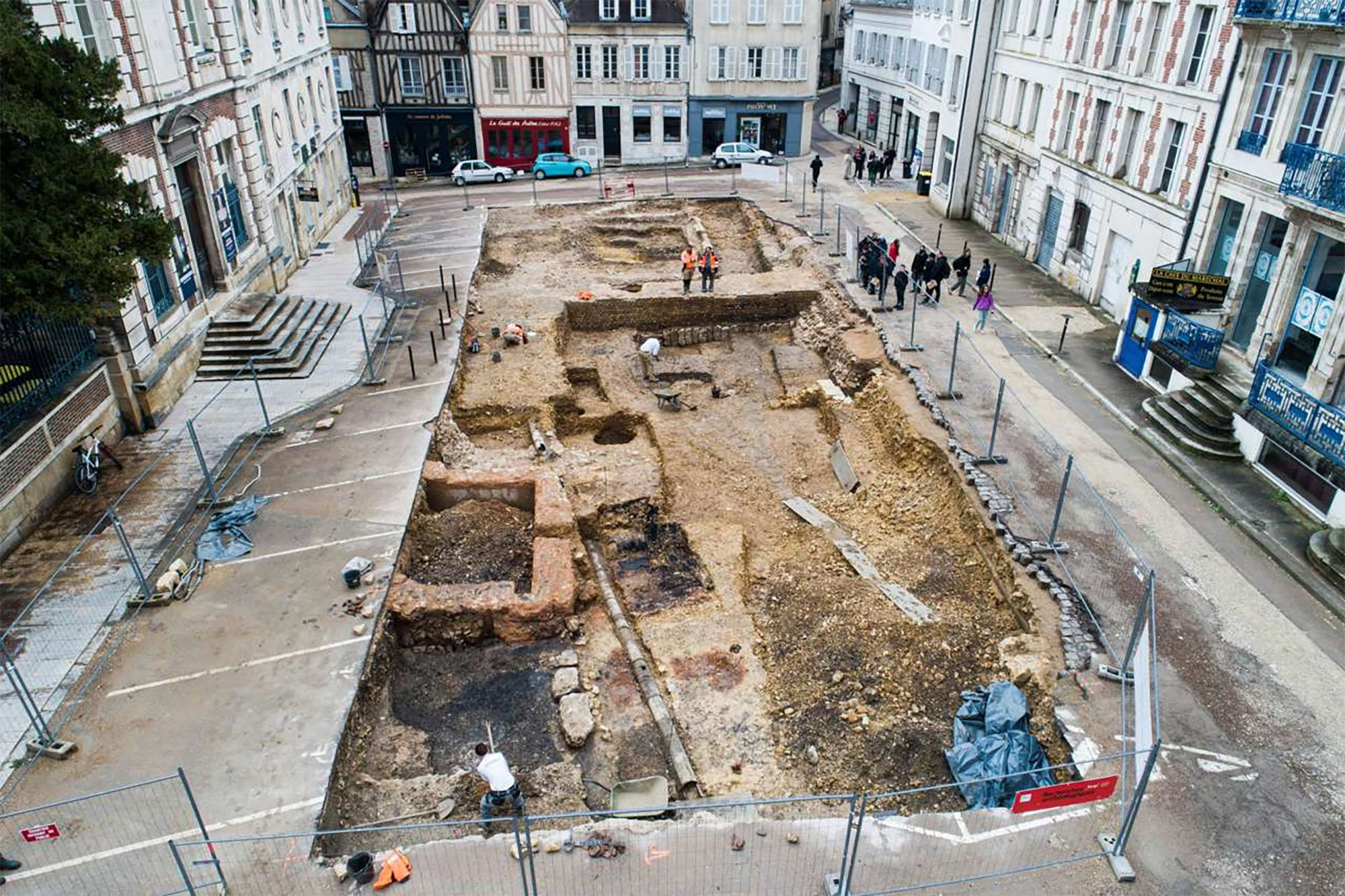
This winter the archaeologists of the INRAP (National Institute of Preventive Archaeological Research) have found a special necropolis in the historic centre of Auxerre (French State), a Roman cemetery for newborn babies or stillbirths. - Oh, good! The necropolis used between... [+]